Rising Interest Rates Mean Deficits Finally Matter
Investors ignored deficits when inflation was low. Now they are paying attention and getting worried.
Investors ignored deficits when inflation was low. Now they are paying attention and getting worried.
The U.S. has long been the lender of last resort to the world. During the emerging-market panics of the 1990s, the global financial crisis of 2007-09 and the pandemic shutdown of 2020, it was the Treasury’s unmatched capacity to borrow that came to the rescue.
Now, the Treasury itself is a source of risk. No, the U.S. isn’t about to default or fail to sell enough bonds at its next auction. But the scale and upward trajectory of U.S. borrowing and absence of any political corrective now threaten markets and the economy in ways they haven’t for at least a generation.
That’s the takeaway from the sudden sharp rise in Treasury yields in recent weeks. The usual suspects can’t explain it: The inflation picture has gotten marginally better, and the Federal Reserve has signalled it’s nearly done raising rates.
Instead, most of the increase is due to the part of yields, called the term premium, which has nothing to do with inflation or short-term rates. Numerous factors affect the term premium, and rising government deficits are a prime suspect.
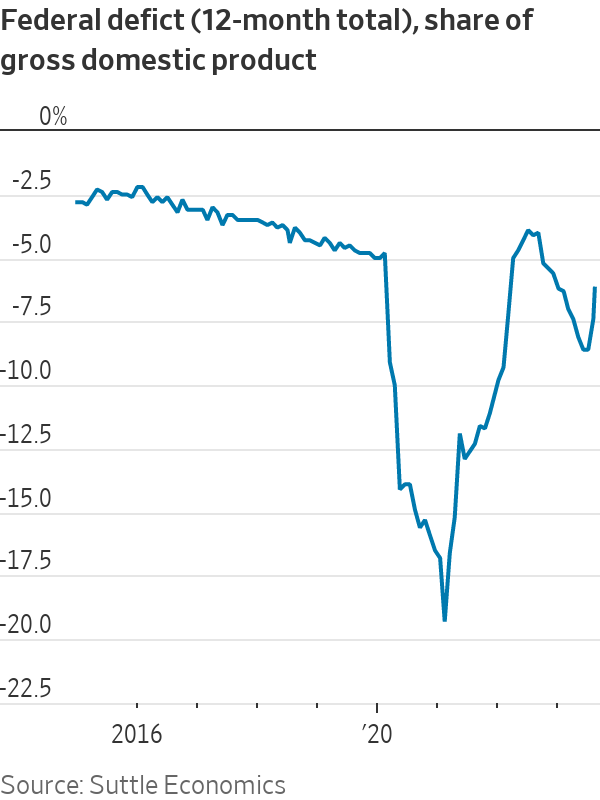
Deficits have been wide for years. Why would they matter now? A better question might be: What took so long?
That larger deficits push up long-term rates had long been economic orthodoxy. But for the past 20 years, interest-rate models that incorporated fiscal policy didn’t work, noted Riccardo Trezzi, a former Fed economist who now runs his own research firm, Underlying Inflation.
That’s understandable. Central banks—worried about too-low inflation and stagnant growth—had kept interest rates around zero while buying up government bonds (“quantitative easing”). Private demand for credit was weak. This trumped any concern about deficits.
“We had a blissful 25 years of not having to worry about this problem,” said Mark Wiedman, senior managing director at BlackRock.
Today, though, central banks are worried about inflation being too high and have stopped buying and in some cases are shedding their bondholdings (“quantitative tightening”). Suddenly, fiscal policy matters again.
To paraphrase Hemingway, deficits can affect interest rates gradually or suddenly. Investors, asked to buy more bonds, gradually make room in their portfolios by buying less of something else, such as equities. Eventually, the risk-adjusted returns of these assets equalise, which means higher bond yields and lower price/earnings ratios on stocks. That has been happening for the past month.
Sometimes, though, markets can move suddenly, such as when Mexico threatened to default in 1994 and Greece did default a decade later. Even in countries that, unlike Mexico or Greece, borrow in currencies they control, interest rates can become hostage to deficits, such as in Canada in the early 1990s or Italy in the 1980s and early 1990s.
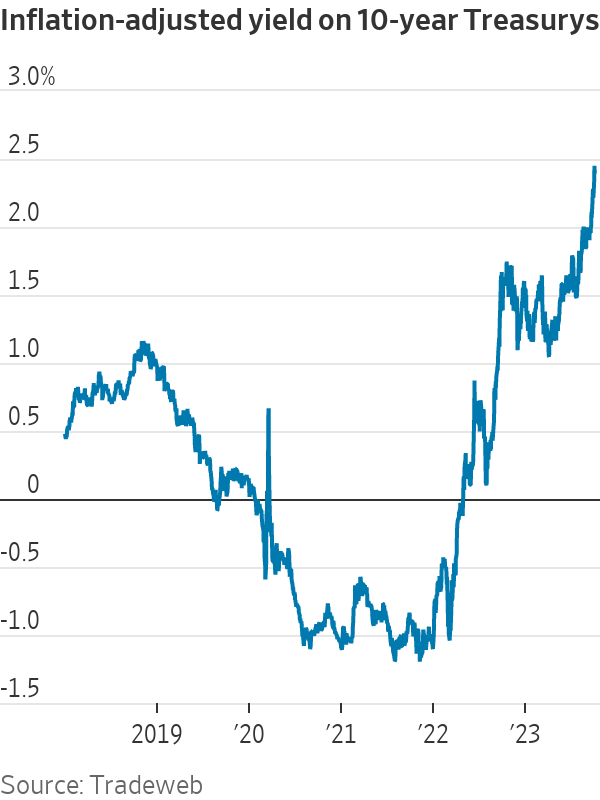
The U.S. isn’t Canada or Italy; it controls the world’s reserve currency, and its inflation and interest rates are mostly driven by domestic, not foreign, factors. On the other hand, the U.S. has also exploited those advantages to accumulate debt and run deficits that are much larger than those of peer economies.
There’s not much sign that this has yet imposed a penalty. Investors still project that the Fed will get inflation down to its 2% goal. At 2.4%, real (inflation-adjusted) Treasury yields are comparable to those in the mid-2000s and lower than in the 1990s, when the U.S. government’s debts and deficits were much lower.
Still, sometimes bad news accumulates below investors’ radar until something brings their collective attention to bear. Could a point come when “all the headlines will be about the fiscal unsustainability of the U.S.?” asked Wiedman. “I don’t hear this today from global investors. But do I think it could happen? Absolutely, that paradigm shift is possible. It’s not that no one shows up to buy Treasurys. It’s that they ask for a much higher yield.”
It’s notable that the recent rise in bond yields came as Fitch Ratings downgraded its U.S. credit rating, Treasury upped the size of its bond auctions, analysts began revising upward this year’s federal deficit, and Congress nearly shut down parts of the government over a failure to pass spending bills.
The federal deficit was over 7% of gross domestic product in fiscal 2023, after adjusting for accounting distortions related to student debt, Barclays analysts noted last week. That’s larger than any deficit since 1930 outside of wars and recessions. And this is occurring at a time of low unemployment and strong economic growth, suggesting that in normal times, “deficits may be much higher,” Barclays added.
Abroad, fiscal policy has clearly begun to matter. Last fall, a proposed U.K. tax cut triggered a surge in British bond yields; the government scrapped the proposal, then resigned. Italian yields have risen since the government last week delayed reducing its deficit to below European guidelines. Trezzi said that for the past decade the European Central Bank had bought more than 100% of net Italian government bond issuance, but that’s coming to an end.
Foreign investors, worried about inflation and deficits, have been selling Italian bonds, while Italian households have been buying, Trezzi said. “With a weakening economy, it is unclear for how long…households can offset the selloff of foreigners.”
Investors looking for U.S. political will to rein in deficits would take note that both former President Donald Trump and President Biden, their parties’ front-runners for the 2024 presidential nomination, have signed deficit-busting legislation and that both of their parties have pledged not tocut the two largest spending programs, Medicare and Social Security, or raise taxes on most households.
They would also notice that the Republican speaker of the House of Representatives was just ousted by rebels in his own party because he had passed a bipartisan spending bill to prevent the government from shutting down. True, the rebels wanted less spending. But shutdowns, Barclays noted, represent “erosion of governance.” This isn’t how a country trying to reassure the bond market acts.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
Multinationals like Starbucks and Marriott are taking a hard look at their Chinese operations—and tempering their outlooks.
For years, global companies showcased their Chinese operations as a source of robust growth. A burgeoning middle class, a stream of people moving to cities, and the creation of new services to cater to them—along with the promise of the further opening of the world’s second-largest economy—drew companies eager to tap into the action.
Then Covid hit, isolating China from much of the world. Chinese leader Xi Jinping tightened control of the economy, and U.S.-China relations hit a nadir. After decades of rapid growth, China’s economy is stuck in a rut, with increasing concerns about what will drive the next phase of its growth.
Though Chinese officials have acknowledged the sputtering economy, they have been reluctant to take more than incremental steps to reverse the trend. Making matters worse, government crackdowns on internet companies and measures to burst the country’s property bubble left households and businesses scarred.
Now, multinational companies are taking a hard look at their Chinese operations and tempering their outlooks. Marriott International narrowed its global revenue per available room growth rate to 3% to 4%, citing continued weakness in China and expectations that demand could weaken further in the third quarter. Paris-based Kering , home to brands Gucci and Saint Laurent, posted a 22% decline in sales in the Asia-Pacific region, excluding Japan, in the first half amid weaker demand in Greater China, which includes Hong Kong and Macau.
Pricing pressure and deflation were common themes in quarterly results. Starbucks , which helped build a coffee culture in China over the past 25 years, described it as one of its most notable international challenges as it posted a 14% decline in sales from that business. As Chinese consumers reconsidered whether to spend money on Starbucks lattes, competitors such as Luckin Coffee increased pressure on the Seattle company. Starbucks executives said in their quarterly earnings call that “unprecedented store expansion” by rivals and a price war hurt profits and caused “significant disruptions” to the operating environment.
Executive anxiety extends beyond consumer companies. Elevator maker Otis Worldwide saw new-equipment orders in China fall by double digits in the second quarter, forcing it to cut its outlook for growth out of Asia. CEO Judy Marks told analysts on a quarterly earnings call that prices in China were down roughly 10% year over year, and she doesn’t see the pricing pressure abating. The company is turning to productivity improvements and cost cutting to blunt the hit.
Add in the uncertainty created by deteriorating U.S.-China relations, and many investors are steering clear. The iShares MSCI China exchange-traded fund has lost half its value since March 2021. Recovery attempts have been short-lived. undefined undefined And now some of those concerns are creeping into the U.S. market. “A decade ago China exposure [for a global company] was a way to add revenue growth to our portfolio,” says Margaret Vitrano, co-manager of large-cap growth strategies at ClearBridge Investments in New York. Today, she notes, “we now want to manage the risk of the China exposure.”
Vitrano expects improvement in 2025, but cautions it will be slow. Uncertainty over who will win the U.S. presidential election and the prospect of higher tariffs pose additional risks for global companies.
For now, China is inching along at roughly 5% economic growth—down from a peak of 14% in 2007 and an average of about 8% in the 10 years before the pandemic. Chinese consumers hit by job losses and continued declines in property values are rethinking spending habits. Businesses worried about policy uncertainty are reluctant to invest and hire.
The trouble goes beyond frugal consumers. Xi is changing the economy’s growth model, relying less on the infrastructure and real estate market that fueled earlier growth. That means investing aggressively in manufacturing and exports as China looks to become more self-reliant and guard against geopolitical tensions.
The shift is hurting western multinationals, with deflationary forces amid burgeoning production capacity. “We have seen the investment community mark down expectations for these companies because they will have to change tack with lower-cost products and services,” says Joseph Quinlan, head of market strategy for the chief investment office at Merrill and Bank of America Private Bank.
Another challenge for multinationals outside of China is stiffened competition as Chinese companies innovate and expand—often with the backing of the government. Local rivals are upping the ante across sectors by building on their knowledge of local consumer preferences and the ability to produce higher-quality products.
Some global multinationals are having a hard time keeping up with homegrown innovation. Auto makers including General Motors have seen sales tumble and struggled to turn profitable as Chinese car shoppers increasingly opt for electric vehicles from BYD or NIO that are similar in price to internal-combustion-engine cars from foreign auto makers.
“China’s electric-vehicle makers have by leaps and bounds surpassed the capabilities of foreign brands who have a tie to the profit pool of internal combustible engines that they don’t want to disrupt,” says Christine Phillpotts, a fund manager for Ariel Investments’ emerging markets strategies.
Chinese companies are often faster than global rivals to market with new products or tweaks. “The cycle can be half of what it is for a global multinational with subsidiaries that need to check with headquarters, do an analysis, and then refresh,” Phillpotts says.
For many companies and investors, next year remains a question mark. Ashland CEO Guillermo Novo said in an August call with analysts that the chemical company was seeing a “big change” in China, with activity slowing and competition on pricing becoming more aggressive. The company, he said, was still trying to grasp the repercussions as it has created uncertainty in its 2025 outlook.
Few companies are giving up. Executives at big global consumer and retail companies show no signs of reducing investment, with most still describing China as a long-term growth market, says Dana Telsey, CEO of Telsey Advisory Group.
Starbucks executives described the long-term opportunity as “significant,” with higher growth and margin opportunities in the future as China’s population continues to move from rural to suburban areas. But they also noted that their approach is evolving and they are in the early stages of exploring strategic partnerships.
Walmart sold its stake in August in Chinese e-commerce giant JD.com for $3.6 billion after an eight-year noncompete agreement expired. Analysts expect it to pump the money into its own Sam’s Club and Walmart China operation, which have benefited from the trend toward trading down in China.
“The story isn’t over for the global companies,” Phillpotts says. “It just means the effort and investment will be greater to compete.”
Corrections & Amplifications
Joseph Quinlan is head of market strategy for the chief investment office at Merrill and Bank of America Private Bank. An earlier version of this article incorrectly used his old title.