Rocket Stock Is the New Meme Trade. Move Over, GameStop.
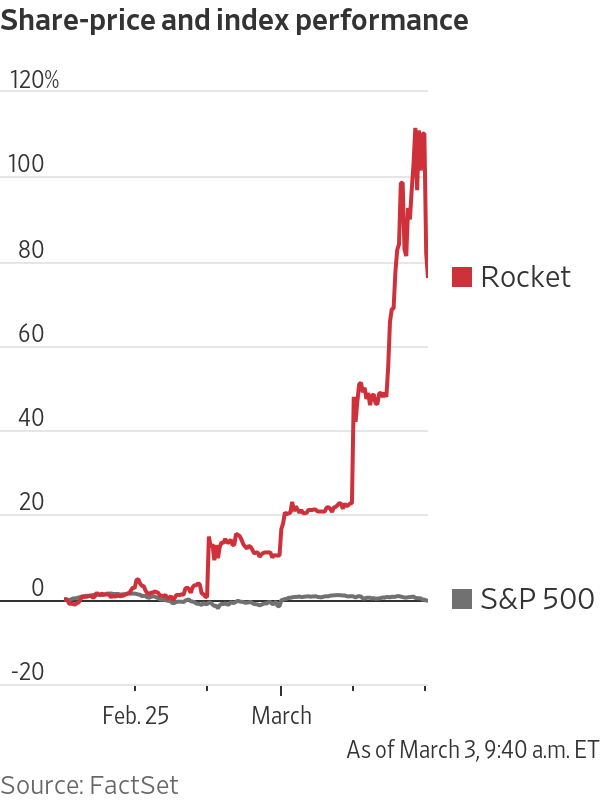
Rocket, the parent of Quicken Loans, has surged 28% this week.
Rocket, the parent of Quicken Loans, has surged 28% this week.
The individual investors that powered GameStop Corp.’s meteoric rise have a new target: Rocket Cos., the parent company of Quicken Loans.
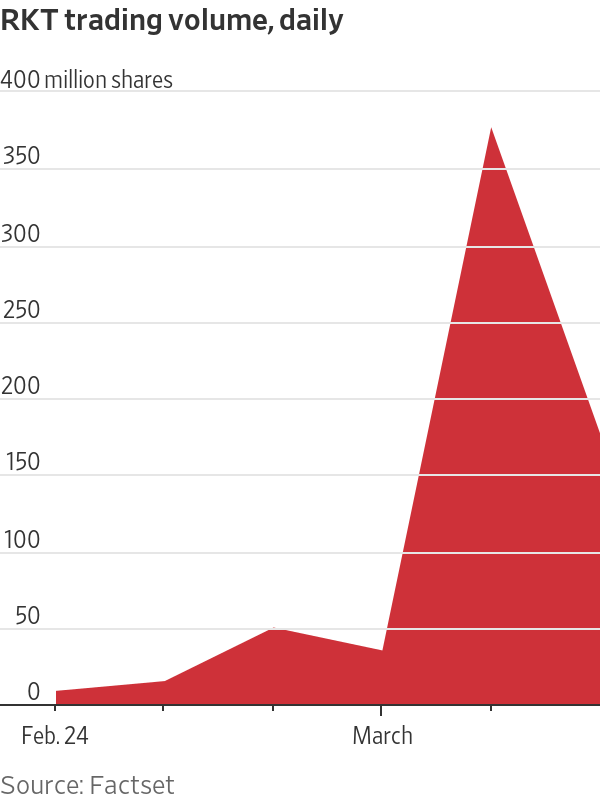
Shares of the mortgage lender surged 28% since the end of last week. Nearly 377 million shares traded hands on Tuesday alone, more than a 10-fold increase from the previous day. After surging 71% on Tuesday, the stock lost some steam on Wednesday, falling 33%, or $13.59, to $28.01.
Like GameStop, Rocket is heavily shorted. As of this week, 46% of its shares available for trading were being shorted by investors betting the price would fall, according to S3 Partners, a data-analytics firm. That was up from about 33% in late January and 17% in mid-September, according to FactSet.
Trading of Rocket shares was halted several times this week because of its volatility.
Individual investors on WallStreetBets, the Reddit community that gave birth to GameStop’s rise, have been encouraging each other to buy the stock in recent days and sharing evidence of their own massive gains. They have relished in the company’s name——Rocket——an apt one for their goal of higher prices.
“The $RKT is fueled and ready for liftoff,” one user wrote early this week.
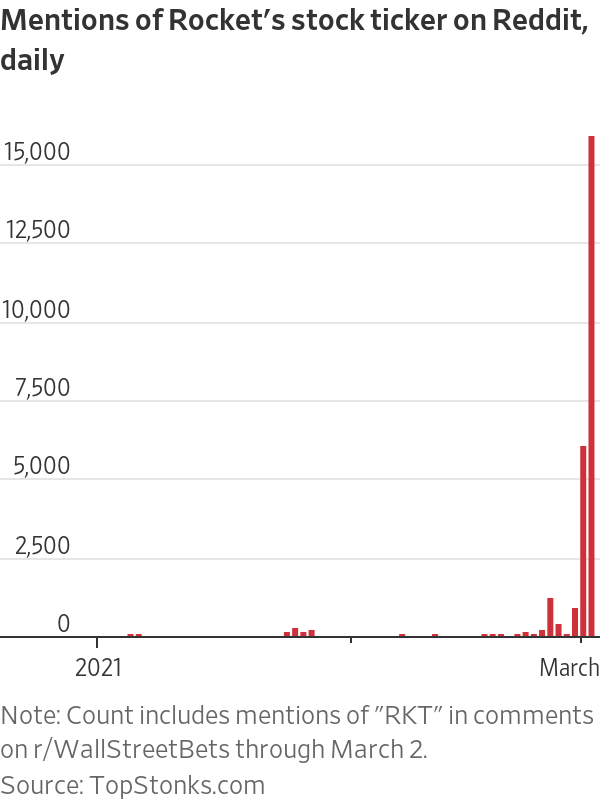
The company stock symbol, RKT, was mentioned in nearly 16,000 Reddit comments on Tuesday, according to data from TopStonks.com, a website that tracks equities mentioned on Reddit. That is up from just over 6,000 on Monday and less than 1,000 on most days last week.
Rocket announced last week it would pay a one-time dividend of $1.11 per share later this month, citing its “highly profitable and capital light business model.” Some investors saw the move as a way to fend off short sellers. Short sellers are obliged to pay any dividends to the broker they borrowed shares from.
The company’s excess capital at the end of the fourth quarter made the dividend possible, Rocket CEO Jay Farner said at a conference Wednesday morning.
“We were pretty proud to be able to offer that to our shareholders,” Mr Farner said. “We think more of dividends as special dividends because we want that flexibility to make the right investment for the long-term growth of the organisation.”
Rocket has other upsides. Rising mortgage rates are boosting earning potential for mortgage lenders just as the crucial spring home-selling season kicks off. The average rate on the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rose to 2.97% recently, its highest level since August.
Detroit-based Rocket is the largest mortgage lender in the U.S., according to research firm Inside Mortgage Finance. Its $323 billion in home loans in 2020 easily surpassed the $221 billion originated by its closest competitor, Wells Fargo & Co. Its large size and strong brand—it ran two Super Bowl commercials—set it apart from other non-bank lenders.
Before Rocket’s blastoff, shares of nonbank mortgage lenders had done little to impress investors in recent months. Some of the lenders that listed their shares on the public market in recent months significantly downsized their offerings. Some never made it to market because of tepid investor interest.
Shares of Rocket hadn’t strayed too far from their listing price of $18 in the seven months since the company’s IPO. The stock soared to more than $31 in its first month but quickly returned to near $20.
The first sign of liftoff came late last week, when Rocket reported impressive fourth-quarter results. Shares rose almost 10% on Friday. The news of a sizable dividend prompted Rocket’s initial jump in stock price, said KBW analyst Bose George.
“The initial move made some sense, but since then, fundamentals haven’t been driving it,” Mr George said. “It’s other factors that we have a harder time assessing.”
Shortly before its public-market debut last summer, Rocket announced an ambitious expansion target: cornering 25% of the mortgage market over the next decade. Its market share currently stands at about a third of that, according to Inside Mortgage Finance.
Rocket said last week that its mortgage originations more than doubled in 2020. It said it expects continued high origination levels despite weakening margins.
The amount lenders earn when they sell each loan has started to drop. Quicken’s gain-on-sale margin was 4.41% in the fourth quarter, down from the third quarter but well above the 3.41% it recorded a year earlier. It expects its first-quarter margin to be between 3.6% and 3.9%.
Cleveland Cavaliers owner Dan Gilbert helped found Quicken Loans in the 1980s and still holds the majority of its shares.
Ali Habhab has watched the stock’s recent ride with interest but doesn’t plan to sell his shares any time soon. Mr. Habhab, who is 25 years old, instead hopes his returns will bring him closer to his goal of retiring at 40. He bought 1,000 shares in Rocket shortly after the company’s IPO in August.
Mr. Habhab, who works in automotive manufacturing, said he was familiar with Quicken Loans long before parent company Rocket decided to go public. Mr. Habhab lives in Detroit, where Rocket is based, and has friends who started careers at the company or one of its subsidiaries.
“With all that factored in, it was a no-brainer to put some of my money where it belongs and where it will grow,” Mr Habhab said.
Another major nonbank mortgage lender, UWM Holdings Corp. is up 27% so far this week.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
CIOs can take steps now to reduce risks associated with today’s IT landscape
As tech leaders race to bring Windows systems back online after Friday’s software update by cybersecurity company CrowdStrike crashed around 8.5 million machines worldwide, experts share with CIO Journal their takeaways for preparing for the next major information technology outage.
IT leaders should hold vendors deeply integrated within IT systems, such as CrowdStrike , to a “very high standard” of development, release quality and assurance, said Neil MacDonald , a Gartner vice president.
“Any security vendor has a responsibility to do extensive regression testing on all versions of Windows before an update is rolled out,” he said.
That involves asking existing vendors to explain how they write software, what testing they do and whether customers may choose how quickly to roll out an update.
“Incidents like this remind all of us in the CIO community of the importance of ensuring availability, reliability and security by prioritizing guardrails such as deployment and testing procedures and practices,” said Amy Farrow, chief information officer of IT automation and security company Infoblox.
While automatically accepting software updates has become the norm—and a recommended security practice—the CrowdStrike outage is a reminder to take a pause, some CIOs said.
“We still should be doing the full testing of packages and upgrades and new features,” said Paul Davis, a field chief information security officer at software development platform maker JFrog . undefined undefined Though it’s not feasible to test every update, especially for as many as hundreds of software vendors, Davis said he makes it a priority to test software patches according to their potential severity and size.
Automation, and maybe even artificial intelligence-based IT tools, can help.
“Humans are not very good at catching errors in thousands of lines of code,” said Jack Hidary, chief executive of AI and quantum company SandboxAQ. “We need AI trained to look for the interdependence of new software updates with the existing stack of software.”
An incident rendering Windows computers unusable is similar to a natural disaster with systems knocked offline, said Gartner’s MacDonald. That’s why businesses should consider natural disaster recovery plans for maintaining the resiliency of their operations.
One way to do that is to set up a “clean room,” or an environment isolated from other systems, to use to bring critical systems back online, according to Chirag Mehta, a cybersecurity analyst at Constellation Research.
Businesses should also hold tabletop exercises to simulate risk scenarios, including IT outages and potential cyber threats, Mehta said.
Companies that back up data regularly were likely less impacted by the CrowdStrike outage, according to Victor Zyamzin, chief business officer of security company Qrator Labs. “Another suggestion for companies, and we’ve been saying that again and again for decades, is that you should have some backup procedure applied, running and regularly tested,” he said.
For any vendor with a significant impact on company operations , MacDonald said companies can review their contracts and look for clauses indicating the vendors must provide reliable and stable software.
“That’s where you may have an advantage to say, if an update causes an outage, is there a clause in the contract that would cover that?” he said.
If it doesn’t, tech leaders can aim to negotiate a discount serving as a form of compensation at renewal time, MacDonald added.
The outage also highlights the importance of insurance in providing companies with bottom-line protection against cyber risks, said Peter Halprin, a partner with law firm Haynes Boone focused on cyber insurance.
This coverage can include protection against business income losses, such as those associated with an outage, whether caused by the insured company or a service provider, Halprin said.
The CrowdStrike update affected only devices running Microsoft Windows-based systems , prompting fresh questions over whether enterprises should rely on Windows computers.
CrowdStrike runs on Windows devices through access to the kernel, the part of an operating system containing a computer’s core functions. That’s not the same for Apple ’s Mac operating system and Linux, which don’t allow the same level of access, said Mehta.
Some businesses have converted to Chromebooks , simple laptops developed by Alphabet -owned Google that run on the Chrome operating system . “Not all of them require deeper access to things,” Mehta said. “What are you doing on your laptop that actually requires Windows?”