The Stocks Investors Are Putting Under the Tree
Shares of retailers including Victoria’s Secret and Foot Locker are surging despite mixed holiday updates
Shares of retailers including Victoria’s Secret and Foot Locker are surging despite mixed holiday updates
Retailers are making modest predictions about the holiday shopping season—and their stocks are going gangbusters in response.
Victoria’s Secret, Foot Locker, Ulta Beauty and Dollar Tree are among the companies that offered somewhat mixed assessments of the state of the shopper last week. Yet each received an ovation from investors.
Traders have piled into stocks en masse since a softer-than-expected inflation reading on Nov. 14 bolstered wagers that the Federal Reserve is done raising interest rates and is poised to cool the economy without tipping it into a recession. Treasury yields have sharply declined as well, giving equities a second wind.
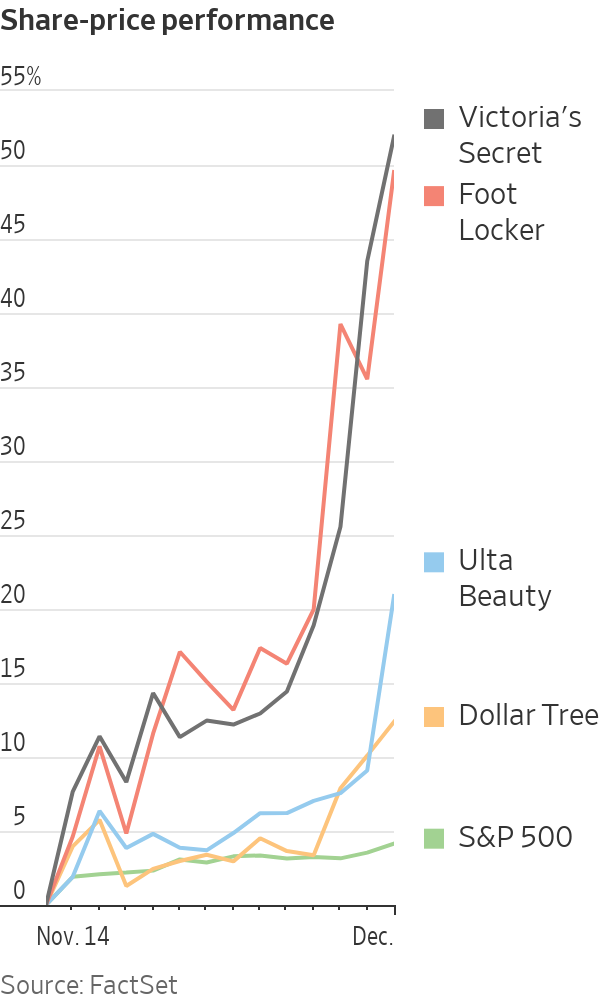
The S&P 500 has risen 4.1% since the report, extending its gains for the year to almost 20%.
Many depressed sectors of the market, such as retailers, have risen even faster. The SPDR S&P Retail exchange-traded fund—which includes 78 retailers, from department stores and other apparel companies, to automotive and drugstores—has jumped about 13%. Victoria’s Secret has soared 52%, Foot Locker is up 50%, Ulta has risen 21% and Dollar Tree has added 12%. (Three of the four stocks have suffered double-digit percentage declines this year.)
Americans slowed their spending in October, according to last week’s consumer-spending data from the Commerce Department. But the early readings from the holiday shopping season have been more encouraging. U.S. shoppers spent $38 billion during the five days from Thanksgiving through the following Monday, up 7.8% from the same period last year, according to Adobe Analytics.
Many investors closely watch consumer spending because it is a major driver of economic growth. If spending is too strong, the Fed could be forced to raise interest rates again. Whereas, if spending is too weak, it could be a sign that the economy is entering a recession.
In the coming days, investors will look at U.S. service-sector activity for November and Friday’s monthly jobs report as they try to assess the strength of the economy and the market’s trajectory.
“The consumer has been resilient throughout it all,” said Jay Woods, chief global strategist at Freedom Capital Markets. “The economic news is now starting to back that up, that, ‘OK, we aren’t going to be in a recession. Things are getting a little bit better.’ And these stocks that had been beaten-down are finally catching a bid.”
Victoria’s Secret posted its second consecutive quarterly loss Wednesday, with the lingerie retailer facing a continued slump in sales. But the company forecast higher sales in the current quarter, sending shares up 14% the next day, their largest one-day percentage gain in more than two years. The stock is down 20% in 2023.
Footwear retailer Foot Locker said Wednesday that Black Friday sales were strong and it forecast an upbeat holiday shopping period, while reporting lower sales and profit for the third quarter. Its shares rose 16% that day, their biggest gain in more than a year, trimming their 2023 decline to 21%.
Cosmetic retailer Ulta on Thursday posted stronger-than-expected sales in the third quarter and raised the lower end of its sales and profit outlook for the year. The shares rose 11% in the following session, their best day since May 2022. They are up 0.6% for the year.
Dollar Tree reported Wednesday that same-store sales growth was weaker than analysts expected, but investors appeared to be encouraged that the discount retailer is seeing increases in customer traffic, even if basket sizes are shrinking. Its shares rose 4.4% that day and are off 11% in 2023.
Another reason why retail stocks have rallied? Warehouses have reduced merchandise, and store shelves aren’t spilling over with discounted goods.
John Augustine, chief investment officer at Huntington Private Bank, said higher interest rates and oil prices made him bearish on retail stocks over the summer. But with an easing macro environment, he believes retailers could be poised to do well.
“It seems like traffic is gonna be there for the holidays,” Augustine said. “Now can retailers make the same profit, earnings per share, with tighter inventory?”
Short sellers are licking their wounds after the recent rally. They lost about $120 million in November betting against the SPDR S&P Retail ETF, according to financial-analytics firm S3 Partners. That compares with a loss of $2.8 million through the first 10 months of the year. Short sellers borrow shares and sell them, expecting to repurchase them at lower prices and collect the difference as profit.
Many retail stocks still generally look cheap compared with the broader market. Victoria’s Secret is trading at 11.8 times its projected earnings over the next 12 months, while Foot Locker is at 16.2. The S&P 500’s multiple is 18.8.
Despite the recent excitement in markets, many investors caution that it is too soon to count on a soft landing for the economy. Jamie Dimon, chief executive of JPMorgan Chase, recently cautioned that inflation could rise further and a recession isn’t off the table.
In the past 11 Fed rate-hiking cycles, recessions have typically started around two years after the Fed begins raising interest rates, according to Deutsche Bank. This hiking cycle started last March.
“It’s not an all-clear resurgence trade that we’re in right now,” said Brock Campbell, head of global research at Newton Investment Management. “This is gonna be a much more idiosyncratic stock picker’s group for a while.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
CIOs can take steps now to reduce risks associated with today’s IT landscape
As tech leaders race to bring Windows systems back online after Friday’s software update by cybersecurity company CrowdStrike crashed around 8.5 million machines worldwide, experts share with CIO Journal their takeaways for preparing for the next major information technology outage.
IT leaders should hold vendors deeply integrated within IT systems, such as CrowdStrike , to a “very high standard” of development, release quality and assurance, said Neil MacDonald , a Gartner vice president.
“Any security vendor has a responsibility to do extensive regression testing on all versions of Windows before an update is rolled out,” he said.
That involves asking existing vendors to explain how they write software, what testing they do and whether customers may choose how quickly to roll out an update.
“Incidents like this remind all of us in the CIO community of the importance of ensuring availability, reliability and security by prioritizing guardrails such as deployment and testing procedures and practices,” said Amy Farrow, chief information officer of IT automation and security company Infoblox.
While automatically accepting software updates has become the norm—and a recommended security practice—the CrowdStrike outage is a reminder to take a pause, some CIOs said.
“We still should be doing the full testing of packages and upgrades and new features,” said Paul Davis, a field chief information security officer at software development platform maker JFrog . undefined undefined Though it’s not feasible to test every update, especially for as many as hundreds of software vendors, Davis said he makes it a priority to test software patches according to their potential severity and size.
Automation, and maybe even artificial intelligence-based IT tools, can help.
“Humans are not very good at catching errors in thousands of lines of code,” said Jack Hidary, chief executive of AI and quantum company SandboxAQ. “We need AI trained to look for the interdependence of new software updates with the existing stack of software.”
An incident rendering Windows computers unusable is similar to a natural disaster with systems knocked offline, said Gartner’s MacDonald. That’s why businesses should consider natural disaster recovery plans for maintaining the resiliency of their operations.
One way to do that is to set up a “clean room,” or an environment isolated from other systems, to use to bring critical systems back online, according to Chirag Mehta, a cybersecurity analyst at Constellation Research.
Businesses should also hold tabletop exercises to simulate risk scenarios, including IT outages and potential cyber threats, Mehta said.
Companies that back up data regularly were likely less impacted by the CrowdStrike outage, according to Victor Zyamzin, chief business officer of security company Qrator Labs. “Another suggestion for companies, and we’ve been saying that again and again for decades, is that you should have some backup procedure applied, running and regularly tested,” he said.
For any vendor with a significant impact on company operations , MacDonald said companies can review their contracts and look for clauses indicating the vendors must provide reliable and stable software.
“That’s where you may have an advantage to say, if an update causes an outage, is there a clause in the contract that would cover that?” he said.
If it doesn’t, tech leaders can aim to negotiate a discount serving as a form of compensation at renewal time, MacDonald added.
The outage also highlights the importance of insurance in providing companies with bottom-line protection against cyber risks, said Peter Halprin, a partner with law firm Haynes Boone focused on cyber insurance.
This coverage can include protection against business income losses, such as those associated with an outage, whether caused by the insured company or a service provider, Halprin said.
The CrowdStrike update affected only devices running Microsoft Windows-based systems , prompting fresh questions over whether enterprises should rely on Windows computers.
CrowdStrike runs on Windows devices through access to the kernel, the part of an operating system containing a computer’s core functions. That’s not the same for Apple ’s Mac operating system and Linux, which don’t allow the same level of access, said Mehta.
Some businesses have converted to Chromebooks , simple laptops developed by Alphabet -owned Google that run on the Chrome operating system . “Not all of them require deeper access to things,” Mehta said. “What are you doing on your laptop that actually requires Windows?”