The U.S. Economy’s Secret Weapon: Seniors With Money to Spend
Americans 65 and older account for record share of spending and are less susceptible to interest rates
Americans 65 and older account for record share of spending and are less susceptible to interest rates
Why has consumer spending proven so resilient as the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates? An important and little-appreciated reason: Consumers are getting older.
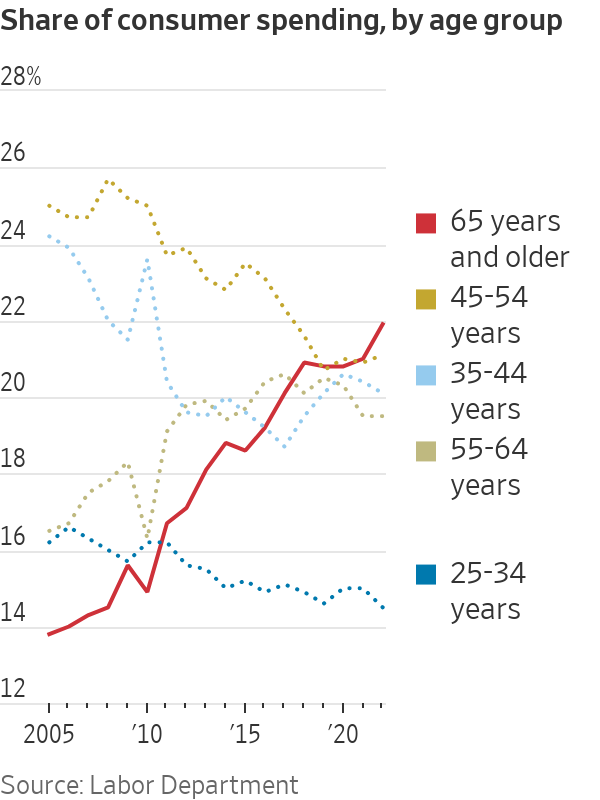
In August, 17.7% of the population was 65 or older, according to the Census Bureau, the highest on record going back to 1920 and up sharply from 13% in 2010. The elderly aren’t just more numerous: Their finances are relatively healthy and they have less need to borrow, such as to buy a house, and are less at risk of layoffs than other consumers.
This has made the elderly a spending force to be reckoned with. Americans age 65 and up accounted for 22% of spending last year, the highest share since records began in 1972 and up from 15% in 2010, according to the Labor Department’s survey of consumer expenditures released in September.
“These are the consumers that will matter over the coming year,” said Susan Sterne, chief economist at Economic Analysis Associates.
“Our large share of older consumers provides a consumption base in times like today when job growth slows, interest rates rise and student-debt loan repayments begin again,” she said.
Seniors’ high spending propensities reflect health, wealth and perhaps lingering psychological effects of the pandemic.
“All my life it was, save for this, save for that,” said Maureen Green, 66, of Cape Cod, Mass. “Now there’s money in the bank and I’m spending in ways that bring me closer to friends and family than I did before.”
Green, a real-estate agent with four grown children living across the country, estimated she is spending 25% more and twice as much time traveling now compared with 2019. She recently traveled to Syracuse, N.Y., to catch a photo exhibit with friends, and toured Rhode Island with her son and his girlfriend.
“The one million Americans who didn’t survive Covid—that’s part of it. That taught me not to let time go by because before I know it, that time won’t be there anymore,” she said.
“The lifestyle of the senior has changed dramatically—they’re more active than ever,” said Marshal Cohen, chief retail adviser of Circana, a research firm specializing in consumer behavior. That has expanded the menu of recreation on which to spend, he said. “They’re riding e-bikes, they’re hiking, they’re traveling. And they’re doing these things for longer than they’ve ever been done.”
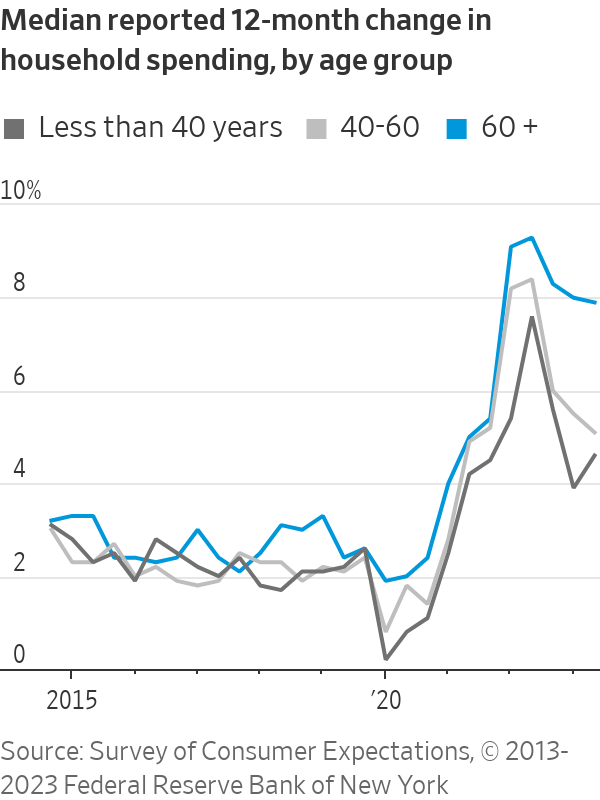
The average household led by someone age 65 and older spent 2.7% more last year than in 2021, adjusted for inflation, according to the Labor Department, compared with 0.7% for under-65 households. Spending by older households is up 34.5% from 1982, compared with 16.5% for younger households.
Comparable data isn’t available for 2023. However, consumers older than 60 reported spending 7.9% more in August than a year earlier, compared with a 5.1% increase among those age 40 to 60 and a 4.6% gain for younger consumers, according to a survey by the New York Fed. The data aren’t adjusted for inflation.
The growing yen to spend by the elderly is amplified by their sheer numbers. The unusually large cohort of baby boomers, the youngest of which are 59, are reaching their retirement years en masse.
American Cruise Lines, which gears its cruises toward older consumers, said it is seeing double-digit sales growth this year, driven largely by boomers. The Guilford, Conn., company this year added three ships to its fleet and expanded its season by a month for some popular routes.
“River cruising has traditionally attracted an older audience, and with more boomers retiring each year, we see both a rapid rate of growth and demand for longer experiences,” said Charles B. Robertson, the company’s president and chief executive.
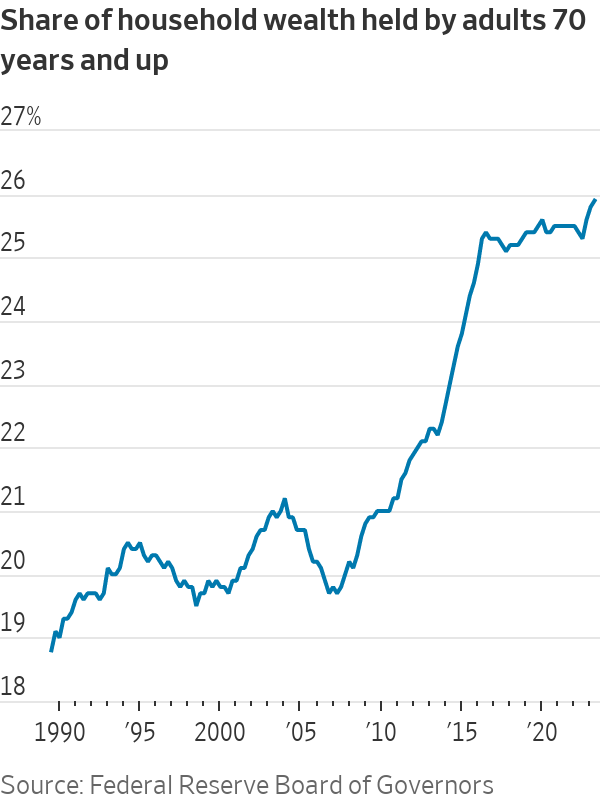
Another factor in the elderly’s favor: relatively strong finances. Americans age 70 and older now hold nearly 26% of household wealth, the highest since records began in 1989, according to the Federal Reserve.
While economists still see a relatively high probability of recession in the coming year, Ed Yardeni, president and chief investment strategist of Yardeni Research, isn’t one of them. An important reason: By the Fed’s reckoning, baby boomers alone have now amassed $77.1 trillion in wealth. “There’s a $77 trillion-wide hole in the theory that consumers’ running out of pandemic savings will sink the economy,” he said.
They have less consumer debt, minimal student debt and are more likely to own their homes outright. Many of those who have mortgages refinanced at the unprecedented low in mortgage rates after the pandemic hit. They are also less likely to need to move due to an expanding family or a new job than Gen Z and Millennials, shielding them from the impact of rising housing costs.
Retirees also received an 8.7% cost-of-living-adjustment bump to Social Security payments in January, the largest single-year increase since 1981, and an automatic adjustment to offset last year’s 9.1% inflation peak.
These factors have cushioned seniors from the twin scourges of inflation and high interest rates. And since most of them are retired, seniors’ spending is less vulnerable to the rise in unemployment that many economists anticipate in coming quarters.
Subscription demand for the Cincinnati Opera’s summer festival this year was surprisingly strong and driven by older patrons, said Todd Bezold, director of marketing.
“Despite the multiyear trend in subscriptions going down, down, down in every art form, we went up this year—by 3%,” he said. That jump in demand came despite a sharp rise in ticket prices to account for several years of inflation. “The vast majority of our subscribers are baby boomers; we know that much.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
CIOs can take steps now to reduce risks associated with today’s IT landscape
As tech leaders race to bring Windows systems back online after Friday’s software update by cybersecurity company CrowdStrike crashed around 8.5 million machines worldwide, experts share with CIO Journal their takeaways for preparing for the next major information technology outage.
IT leaders should hold vendors deeply integrated within IT systems, such as CrowdStrike , to a “very high standard” of development, release quality and assurance, said Neil MacDonald , a Gartner vice president.
“Any security vendor has a responsibility to do extensive regression testing on all versions of Windows before an update is rolled out,” he said.
That involves asking existing vendors to explain how they write software, what testing they do and whether customers may choose how quickly to roll out an update.
“Incidents like this remind all of us in the CIO community of the importance of ensuring availability, reliability and security by prioritizing guardrails such as deployment and testing procedures and practices,” said Amy Farrow, chief information officer of IT automation and security company Infoblox.
While automatically accepting software updates has become the norm—and a recommended security practice—the CrowdStrike outage is a reminder to take a pause, some CIOs said.
“We still should be doing the full testing of packages and upgrades and new features,” said Paul Davis, a field chief information security officer at software development platform maker JFrog . undefined undefined Though it’s not feasible to test every update, especially for as many as hundreds of software vendors, Davis said he makes it a priority to test software patches according to their potential severity and size.
Automation, and maybe even artificial intelligence-based IT tools, can help.
“Humans are not very good at catching errors in thousands of lines of code,” said Jack Hidary, chief executive of AI and quantum company SandboxAQ. “We need AI trained to look for the interdependence of new software updates with the existing stack of software.”
An incident rendering Windows computers unusable is similar to a natural disaster with systems knocked offline, said Gartner’s MacDonald. That’s why businesses should consider natural disaster recovery plans for maintaining the resiliency of their operations.
One way to do that is to set up a “clean room,” or an environment isolated from other systems, to use to bring critical systems back online, according to Chirag Mehta, a cybersecurity analyst at Constellation Research.
Businesses should also hold tabletop exercises to simulate risk scenarios, including IT outages and potential cyber threats, Mehta said.
Companies that back up data regularly were likely less impacted by the CrowdStrike outage, according to Victor Zyamzin, chief business officer of security company Qrator Labs. “Another suggestion for companies, and we’ve been saying that again and again for decades, is that you should have some backup procedure applied, running and regularly tested,” he said.
For any vendor with a significant impact on company operations , MacDonald said companies can review their contracts and look for clauses indicating the vendors must provide reliable and stable software.
“That’s where you may have an advantage to say, if an update causes an outage, is there a clause in the contract that would cover that?” he said.
If it doesn’t, tech leaders can aim to negotiate a discount serving as a form of compensation at renewal time, MacDonald added.
The outage also highlights the importance of insurance in providing companies with bottom-line protection against cyber risks, said Peter Halprin, a partner with law firm Haynes Boone focused on cyber insurance.
This coverage can include protection against business income losses, such as those associated with an outage, whether caused by the insured company or a service provider, Halprin said.
The CrowdStrike update affected only devices running Microsoft Windows-based systems , prompting fresh questions over whether enterprises should rely on Windows computers.
CrowdStrike runs on Windows devices through access to the kernel, the part of an operating system containing a computer’s core functions. That’s not the same for Apple ’s Mac operating system and Linux, which don’t allow the same level of access, said Mehta.
Some businesses have converted to Chromebooks , simple laptops developed by Alphabet -owned Google that run on the Chrome operating system . “Not all of them require deeper access to things,” Mehta said. “What are you doing on your laptop that actually requires Windows?”