To Find Winning Stocks, Investors Often Focus on the Laggards. They Shouldn’t.
These stocks are getting hit for a reason. Instead, focus on stocks that show ‘relative strength.’ Here’s how.
These stocks are getting hit for a reason. Instead, focus on stocks that show ‘relative strength.’ Here’s how.
A lot of investors get stock-picking wrong before they even get started: Instead of targeting the top-performing stocks in the market, they focus on the laggards—widely known companies that look as if they are on sale after a period of stock-price weakness.
But these weak performers usually are going down for good reasons, such as for deteriorating sales and earnings, market-share losses or mutual-fund managers who are unwinding positions.
Decades of Investor’s Business Daily research shows these aren’t the stocks that tend to become stock-market leaders. The stocks that reward investors with handsome gains for months or years are more often already the strongest price performers, usually because of outstanding earnings and sales growth and increasing fund ownership.
Of course, many investors already chase performance and pour money into winning stocks. So how can a discerning investor find the winning stocks that have more room to run?
Enter “relative strength”—the notion that strength begets more strength. Relative strength measures stocks’ recent performance relative to the overall market. Investing in stocks with high relative strength means going with the winners, rather than picking stocks in hopes of a rebound. Why bet on a last-place team when you can wager on the leader?
One of the easiest ways to identify the strongest price performers is with IBD’s Relative Strength Rating. Ranked on a scale of 1-99, a stock with an RS rating of 99 has outperformed 99% of all stocks based on 12-month price performance.
To capitalise on relative strength, an investor’s search should be focused on stocks with RS ratings of at least 80.
But beware: While the goal is to buy stocks that are performing better than the overall market, stocks with the highest RS ratings aren’t always the best to buy. No doubt, some stocks extend rallies for years. But others will be too far into their price run-up and ready to start a longer-term price decline.
Thus, there is a limit to chasing performance. To avoid this pitfall, investors should focus on stocks that have strong relative strength but have seen a moderate price decline and are just coming out of weeks or months of trading within a limited range. This range will vary by stock, but IBD research shows that most good trading patterns can show declines of up to one-third.
Here, a relative strength line on a chart may be helpful for confirming an RS rating’s buy signal. Offered on some stock-charting tools, including IBD’s, the line is a way to visualise relative strength by comparing a stock’s price performance relative to the movement of the S&P 500 or other benchmark.
When the line is sloping upward, it means the stock is outperforming the benchmark. When it is sloping downward, the stock is lagging behind the benchmark. One reason the RS line is helpful is that the line can rise even when a stock price is falling, meaning its value is falling at a slower pace than the benchmark.
The value of relative strength could be seen in Google parent Alphabet in January 2020, when its RS rating was 89 before it started a 10-month run when the stock rose 64%. Meta Platforms ’ RS rating was 96 before the Facebook parent hit new highs in March 2023 and ran up 65% in four months. Abercrombie & Fitch , one of 2023’s best-performing stocks, had a 94 rating before it soared 342% in nine months starting in June 2023.
Those stocks weren’t flukes. In a study of the biggest stock-market winners from the early 1950s through 2008, the average RS rating of the best performers before they began their major price runs was 87.
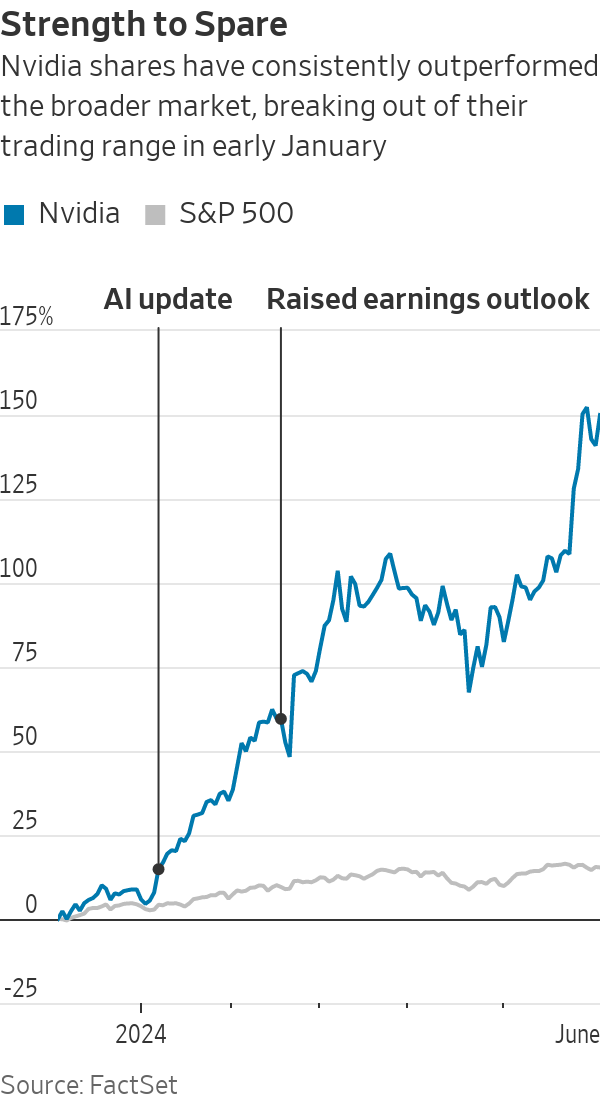
To see relative strength in action, consider Nvidia . The chip stock was an established leader, having shot up 365% from its October 2022 low to its high of $504.48 in late August 2023.
But then it spent the next four months rangebound—giving up some ground, then gaining some back. Through this period, shares held between $392.30 and the August peak, declining no more than 22% from top to bottom.
On Jan. 8, Nvidia broke out of its trading range to new highs. The previous session, Nvidia’s RS rating was 97. And that week, the stock’s relative strength line hit new highs. The catalyst: Investors cheered the company’s update on its latest advancements in artificial intelligence.
Nvidia then rose 16% on Feb. 22 after the company said earnings for the January-ended quarter soared 486% year over year to $5.16 a share. Revenue more than tripled to $22.1 billion. It also significantly raised its earnings and revenue guidance for the quarter that was to end in April. In all, Nvidia climbed 89% from Jan. 5 to its March 7 close.
And the stock has continued to run up, surging past $1,000 a share in late May after the company exceeded that guidance for the April-ended quarter and delivered record revenue of $26 billion and record net profit of $14.88 billion.
Ken Shreve is a senior markets writer at Investor’s Business Daily. Follow him on X @IBD_KShreve for more stock-market analysis and insights, or contact him at ken.shreve@investors.com .
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
CIOs can take steps now to reduce risks associated with today’s IT landscape
As tech leaders race to bring Windows systems back online after Friday’s software update by cybersecurity company CrowdStrike crashed around 8.5 million machines worldwide, experts share with CIO Journal their takeaways for preparing for the next major information technology outage.
IT leaders should hold vendors deeply integrated within IT systems, such as CrowdStrike , to a “very high standard” of development, release quality and assurance, said Neil MacDonald , a Gartner vice president.
“Any security vendor has a responsibility to do extensive regression testing on all versions of Windows before an update is rolled out,” he said.
That involves asking existing vendors to explain how they write software, what testing they do and whether customers may choose how quickly to roll out an update.
“Incidents like this remind all of us in the CIO community of the importance of ensuring availability, reliability and security by prioritizing guardrails such as deployment and testing procedures and practices,” said Amy Farrow, chief information officer of IT automation and security company Infoblox.
While automatically accepting software updates has become the norm—and a recommended security practice—the CrowdStrike outage is a reminder to take a pause, some CIOs said.
“We still should be doing the full testing of packages and upgrades and new features,” said Paul Davis, a field chief information security officer at software development platform maker JFrog . undefined undefined Though it’s not feasible to test every update, especially for as many as hundreds of software vendors, Davis said he makes it a priority to test software patches according to their potential severity and size.
Automation, and maybe even artificial intelligence-based IT tools, can help.
“Humans are not very good at catching errors in thousands of lines of code,” said Jack Hidary, chief executive of AI and quantum company SandboxAQ. “We need AI trained to look for the interdependence of new software updates with the existing stack of software.”
An incident rendering Windows computers unusable is similar to a natural disaster with systems knocked offline, said Gartner’s MacDonald. That’s why businesses should consider natural disaster recovery plans for maintaining the resiliency of their operations.
One way to do that is to set up a “clean room,” or an environment isolated from other systems, to use to bring critical systems back online, according to Chirag Mehta, a cybersecurity analyst at Constellation Research.
Businesses should also hold tabletop exercises to simulate risk scenarios, including IT outages and potential cyber threats, Mehta said.
Companies that back up data regularly were likely less impacted by the CrowdStrike outage, according to Victor Zyamzin, chief business officer of security company Qrator Labs. “Another suggestion for companies, and we’ve been saying that again and again for decades, is that you should have some backup procedure applied, running and regularly tested,” he said.
For any vendor with a significant impact on company operations , MacDonald said companies can review their contracts and look for clauses indicating the vendors must provide reliable and stable software.
“That’s where you may have an advantage to say, if an update causes an outage, is there a clause in the contract that would cover that?” he said.
If it doesn’t, tech leaders can aim to negotiate a discount serving as a form of compensation at renewal time, MacDonald added.
The outage also highlights the importance of insurance in providing companies with bottom-line protection against cyber risks, said Peter Halprin, a partner with law firm Haynes Boone focused on cyber insurance.
This coverage can include protection against business income losses, such as those associated with an outage, whether caused by the insured company or a service provider, Halprin said.
The CrowdStrike update affected only devices running Microsoft Windows-based systems , prompting fresh questions over whether enterprises should rely on Windows computers.
CrowdStrike runs on Windows devices through access to the kernel, the part of an operating system containing a computer’s core functions. That’s not the same for Apple ’s Mac operating system and Linux, which don’t allow the same level of access, said Mehta.
Some businesses have converted to Chromebooks , simple laptops developed by Alphabet -owned Google that run on the Chrome operating system . “Not all of them require deeper access to things,” Mehta said. “What are you doing on your laptop that actually requires Windows?”