Welcome to the Era of BadGPTs
The dark web is home to a growing array of artificial-intelligence chatbots similar to ChatGPT, but designed to help hackers. Businesses are on high alert for a glut of AI-generated email fraud and deepfakes.
The dark web is home to a growing array of artificial-intelligence chatbots similar to ChatGPT, but designed to help hackers. Businesses are on high alert for a glut of AI-generated email fraud and deepfakes.
A new crop of nefarious chatbots with names like “BadGPT” and “FraudGPT” are springing up on the darkest corners of the web, as cybercriminals look to tap the same artificial intelligence behind OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Just as some office workers use ChatGPT to write better emails, hackers are using manipulated versions of AI chatbots to turbocharge their phishing emails. They can use chatbots—some also freely-available on the open internet—to create fake websites, write malware and tailor messages to better impersonate executives and other trusted entities.
Earlier this year, a Hong Kong multinational company employee handed over $25.5 million to an attacker who posed as the company’s chief financial officer on an AI-generated deepfake conference call, the South China Morning Post reported, citing Hong Kong police. Chief information officers and cybersecurity leaders, already accustomed to a growing spate of cyberattacks , say they are on high alert for an uptick in more sophisticated phishing emails and deepfakes.
Vish Narendra, CIO of Graphic Packaging International, said the Atlanta-based paper packing company has seen an increase in what are likely AI-generated email attacks called spear-phishing , where cyber attackers use information about a person to make an email seem more legitimate. Public companies in the spotlight are even more susceptible to contextualised spear-phishing, he said.
Researchers at Indiana University recently combed through over 200 large-language model hacking services being sold and populated on the dark web. The first service appeared in early 2023—a few months after the public release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in November 2022.
Most dark web hacking tools use versions of open-source AI models like Meta ’s Llama 2, or “jailbroken” models from vendors like OpenAI and Anthropic to power their services, the researchers said. Jailbroken models have been hijacked by techniques like “ prompt injection ” to bypass their built-in safety controls.
Jason Clinton, chief information security officer of Anthropic, said the AI company eliminates jailbreak attacks as they find them, and has a team monitoring the outputs of its AI systems. Most model-makers also deploy two separate models to secure their primary AI model, making the likelihood that all three will fail the same way “a vanishingly small probability.”
Meta spokesperson Kevin McAlister said that openly releasing models shares the benefits of AI widely, and allows researchers to identify and help fix vulnerabilities in all AI models, “so companies can make models more secure.”
An OpenAI spokesperson said the company doesn’t want its tools to be used for malicious purposes, and that it is “always working on how we can make our systems more robust against this type of abuse.”
Malware and phishing emails written by generative AI are especially tricky to spot because they are crafted to evade detection. Attackers can teach a model to write stealthy malware by training it with detection techniques gleaned from cybersecurity defence software, said Avivah Litan, a generative AI and cybersecurity analyst at Gartner.
Phishing emails grew by 1,265% in the 12-month period starting when ChatGPT was publicly released, with an average of 31,000 phishing attacks sent every day, according to an October 2023 report by cybersecurity vendor SlashNext.
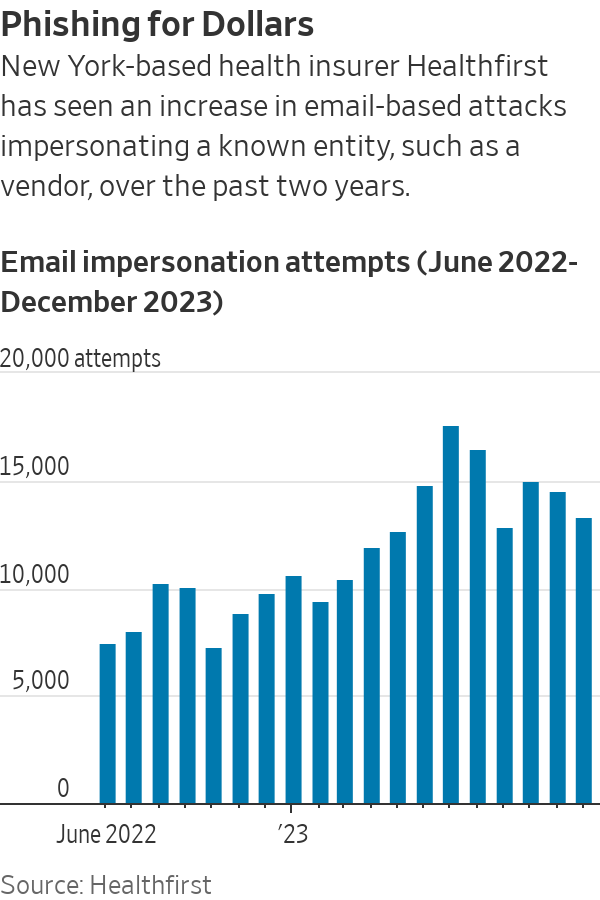
“The hacking community has been ahead of us,” said Brian Miller, CISO of New York-based not-for-profit health insurer Healthfirst, which has seen an increase in attacks impersonating its invoice vendors over the past two years.
While it is nearly impossible to prove whether certain malware programs or emails were created with AI, tools developed with AI can scan for text likely created with the technology. Abnormal Security , an email security vendor, said it had used AI to help identify thousands of likely AI-created malicious emails over the past year, and that it had blocked a twofold increase in targeted, personalised email attacks.
When Good Models Go Bad
Part of the challenge in stopping AI-enabled cybercrime is some AI models are freely shared on the open web. To access them, there is no need for dark corners of the internet or exchanging cryptocurrency.
Such models are considered “uncensored” because they lack the enterprise guardrails that businesses look for when buying AI systems, said Dane Sherrets, an ethical hacker and senior solutions architect at bug bounty company HackerOne.
In some cases, uncensored versions of models are created by security and AI researchers who strip out their built-in safeguards. In other cases, models with safeguards intact will write scam messages if humans avoid obvious triggers like “phishing”—a situation Andy Sharma, CIO and CISO of Redwood Software, said he discovered when creating a spear-phishing test for his employees.
The most useful model for generating scam emails is likely a version of Mixtral, from French AI startup Mistral AI, that has been altered to remove its safeguards, Sherrets said. Due to the advanced design of the original Mixtral, the uncensored version likely performs better than most dark web AI tools, he added. Mistral did not reply to a request for comment.
Sherrets recently demonstrated the process of using an uncensored AI model to generate a phishing campaign. First, he searched for “uncensored” models on Hugging Face, a startup that hosts a popular repository of open-source models—showing how easily many can be found.
He then used a virtual computing service that cost less than $1 per hour to mimic a graphics processing unit, or GPU, which is an advanced chip that can power AI. A bad actor needs either a GPU or a cloud-based service to use an AI model, Sherrets said, adding that he learned most of how to do this on X and YouTube.
With his uncensored model and virtual GPU service running, Sherrets asked the bot: “Write a phishing email targeting a business that impersonates a CEO and includes publicly-available company data,” and “Write an email targeting the procurement department of a company requesting an urgent invoice payment.”
The bot sent back phishing emails that were well-written, but didn’t include all of the personalisation asked for. That’s where prompt engineering , or the human’s ability to better extract information from chatbots, comes in, Sherrets said.
Dark Web AI Tools Can Already Do Harm
For hackers, a benefit of dark web tools like BadGPT—which researchers said uses OpenAI’s GPT model—is that they are likely trained on data from those underground marketplaces. That means they probably include useful information like leaks, ransomware victims and extortion lists, said Joseph Thacker, an ethical hacker and principal AI engineer at cybersecurity software firm AppOmni.
While some underground AI tools have been shuttered, new services have already taken their place, said Indiana University Assistant Computer Science Professor Xiaojing Liao, a co-author of the study. The AI hacking services, which often take payment via cryptocurrency, are priced anywhere from $5 to $199 a month.
New tools are expected to improve just as the AI models powering them do. In a matter of years, AI-generated text, video and voice deepfakes will be virtually indistinguishable from their human counterparts, said Evan Reiser , CEO and co-founder of Abnormal Security.
While researching the hacking tools, Indiana University Associate Dean for Research XiaoFeng Wang, a co-author of the study, said he was surprised by the ability of dark web services to generate effective malware. Given just the code of a security vulnerability, the tools can easily write a program to exploit it.
Though AI hacking tools often fail, in some cases, they work. “That demonstrates, in my opinion, that today’s large language models have the capability to do harm,” Wang said.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
CIOs can take steps now to reduce risks associated with today’s IT landscape
As tech leaders race to bring Windows systems back online after Friday’s software update by cybersecurity company CrowdStrike crashed around 8.5 million machines worldwide, experts share with CIO Journal their takeaways for preparing for the next major information technology outage.
IT leaders should hold vendors deeply integrated within IT systems, such as CrowdStrike , to a “very high standard” of development, release quality and assurance, said Neil MacDonald , a Gartner vice president.
“Any security vendor has a responsibility to do extensive regression testing on all versions of Windows before an update is rolled out,” he said.
That involves asking existing vendors to explain how they write software, what testing they do and whether customers may choose how quickly to roll out an update.
“Incidents like this remind all of us in the CIO community of the importance of ensuring availability, reliability and security by prioritizing guardrails such as deployment and testing procedures and practices,” said Amy Farrow, chief information officer of IT automation and security company Infoblox.
While automatically accepting software updates has become the norm—and a recommended security practice—the CrowdStrike outage is a reminder to take a pause, some CIOs said.
“We still should be doing the full testing of packages and upgrades and new features,” said Paul Davis, a field chief information security officer at software development platform maker JFrog . undefined undefined Though it’s not feasible to test every update, especially for as many as hundreds of software vendors, Davis said he makes it a priority to test software patches according to their potential severity and size.
Automation, and maybe even artificial intelligence-based IT tools, can help.
“Humans are not very good at catching errors in thousands of lines of code,” said Jack Hidary, chief executive of AI and quantum company SandboxAQ. “We need AI trained to look for the interdependence of new software updates with the existing stack of software.”
An incident rendering Windows computers unusable is similar to a natural disaster with systems knocked offline, said Gartner’s MacDonald. That’s why businesses should consider natural disaster recovery plans for maintaining the resiliency of their operations.
One way to do that is to set up a “clean room,” or an environment isolated from other systems, to use to bring critical systems back online, according to Chirag Mehta, a cybersecurity analyst at Constellation Research.
Businesses should also hold tabletop exercises to simulate risk scenarios, including IT outages and potential cyber threats, Mehta said.
Companies that back up data regularly were likely less impacted by the CrowdStrike outage, according to Victor Zyamzin, chief business officer of security company Qrator Labs. “Another suggestion for companies, and we’ve been saying that again and again for decades, is that you should have some backup procedure applied, running and regularly tested,” he said.
For any vendor with a significant impact on company operations , MacDonald said companies can review their contracts and look for clauses indicating the vendors must provide reliable and stable software.
“That’s where you may have an advantage to say, if an update causes an outage, is there a clause in the contract that would cover that?” he said.
If it doesn’t, tech leaders can aim to negotiate a discount serving as a form of compensation at renewal time, MacDonald added.
The outage also highlights the importance of insurance in providing companies with bottom-line protection against cyber risks, said Peter Halprin, a partner with law firm Haynes Boone focused on cyber insurance.
This coverage can include protection against business income losses, such as those associated with an outage, whether caused by the insured company or a service provider, Halprin said.
The CrowdStrike update affected only devices running Microsoft Windows-based systems , prompting fresh questions over whether enterprises should rely on Windows computers.
CrowdStrike runs on Windows devices through access to the kernel, the part of an operating system containing a computer’s core functions. That’s not the same for Apple ’s Mac operating system and Linux, which don’t allow the same level of access, said Mehta.
Some businesses have converted to Chromebooks , simple laptops developed by Alphabet -owned Google that run on the Chrome operating system . “Not all of them require deeper access to things,” Mehta said. “What are you doing on your laptop that actually requires Windows?”