Surging Nvidia Stock Keeps Drawing In More Believers
The chip company that is cashing in on the market’s artificial-intelligence obsession seems to many investors like an unstoppable force
The chip company that is cashing in on the market’s artificial-intelligence obsession seems to many investors like an unstoppable force
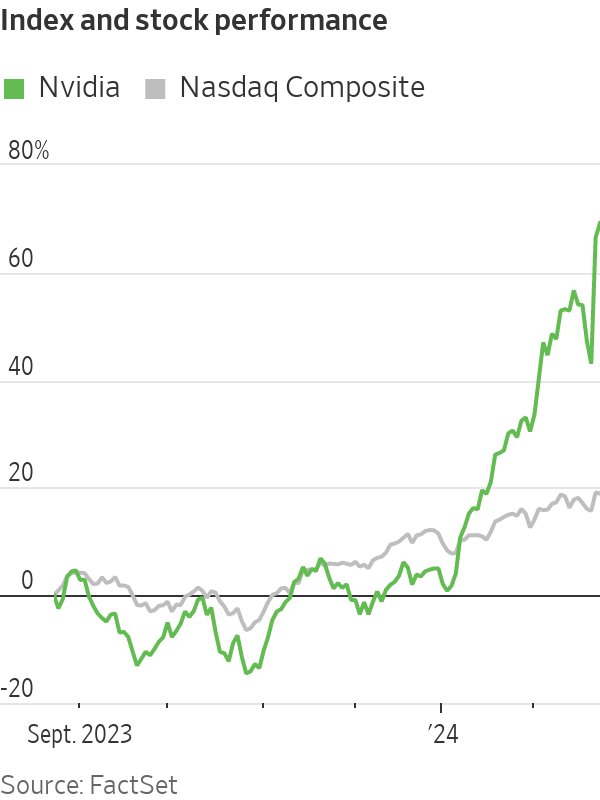
Nvidia ’s historic run is minting profits for investors big and small . Many are betting the boom is just beginning.
They are piling into trades that the chipmaker’s shares, which have more than tripled over the past year , are headed still higher. Some have turned to the options market to look for ways to turbocharge their bets on artificial intelligence after a blockbuster earnings report sent the stock up 17% over the past two days.
The exuberance reflects hope that the company is the vanguard of wide adoption of artificial intelligence—and an intense fear of missing out among investors who have sat on the sidelines while the company’s valuation has eclipsed $2 trillion .
With the help of Nvidia, stocks have stormed into 2024 . The S&P 500, which has chalked up fresh records in recent weeks, is up 6.7%. That is the index’s second-best performance for this time period over the past 10 years. The gains were only surpassed by an 11% increase in 2019.
Nvidia has contributed to about a quarter of those gains, according to S&P Dow Jones Indices.
The Nasdaq, too, is up 6.6% this year and neared a record Friday. The tech-heavy index has been boosted by Nvidia, which this week tacked on $277 billion in additional market value, along with six other tech titans collectively known as the Magnificent Seven.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is up 3.8% this year and has hit repeated records in recent weeks.
“You look at these numbers and what this company’s done—it’s almost without precedent,” said Mike Ogborne, founder of San Francisco-based hedge fund Ogborne Capital Management, who counts Nvidia among his top five biggest holdings . “It is nothing short of amazing.”
Ogborne compared AI with the launch of the internet more than two decades ago, which kick-started a technology craze that lasted years.
“It’s exciting,” Ogborne said. “It’s great for America.”
Tamar June in Reno, Nev., is one investor along for Nvidia’s furious stock-market ascent. Since the 1990s, the 61-year-old software-company chief executive has been buying shares of tech firms, including Apple , Microsoft , Cisco, Intel and Oracle . June had been familiar with Nvidia for some time but in recent years kept reading about the chip company in the news. She liked that it was profitable and growing.
June decided to purchase some shares in 2022 at about $260, then watched the stock erase more than half of its value later that year. She held on, knowing that Nvidia’s graphics processing units were in high demand for cloud computing. Then, an AI frenzy hit the stock market in 2023, sending Nvidia’s stock soaring.
Now, Nvidia shares are closing in on $800, and June is looking for opportunities to buy more. She isn’t fazed by worries that the AI boom is bound to come crashing down. June experienced the bursting of the dot-com bubble and the 2008 financial crisis—and watched stocks bounce back to new highs.
“I think it’s still in the beginning stages,” June said of AI developments. “There’s still a lot of headroom for technology because our whole future depends on it.”
A herd of investors chased Nvidia while it raced toward its $2 trillion valuation.
At Robinhood Markets , Nvidia was the most purchased stock by customers on a net basis and received the heaviest notional trading volumes over the past month, according to Stephanie Guild, head of investment strategy at the digital brokerage.
The rise drove many traders to pile into the company’s options, a risky corner of the market notorious for boom-and-bust trades.
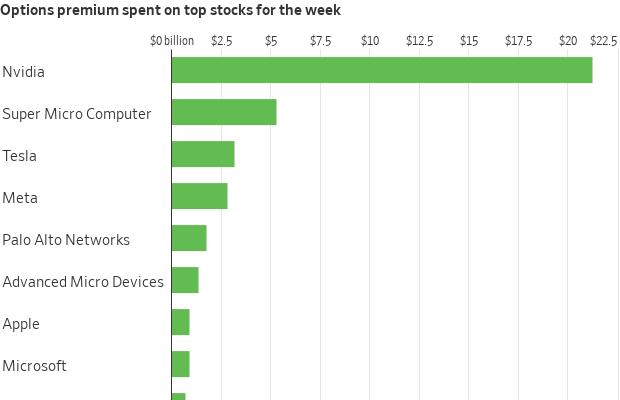
Nvidia has also morphed into one of the most popular trades in this market, with traders placing more than $20 billion in stock-options bets tied to the company over the past week, according to Cboe Global Markets data. That was more than what they spent on Tesla , Meta Platforms , Microsoft, Apple, Amazon and Alphabet combined.
Call options, contracts that confer the right to buy shares at a specific price, were particularly popular. And many of the trades appeared to suggest that investors were fearful of missing out on bigger gains to come. Some of the most active trades Friday were calls pegged to the shares jumping to $800 or $850, up from their closing price of $788.17. Betting against the shares has been a losing game , leading many investors to throw in the towel on bearish wagers.
The values of many of these options bets exploded while Nvidia soared, rewarding those who piled in. The big gains also enticed others to join in the trades while the stock’s rally continued.
“There’s a snowball effect,” said Henry Schwartz, a vice president at exchange-operator Cboe Global Markets, of the options activity surrounding Nvidia.
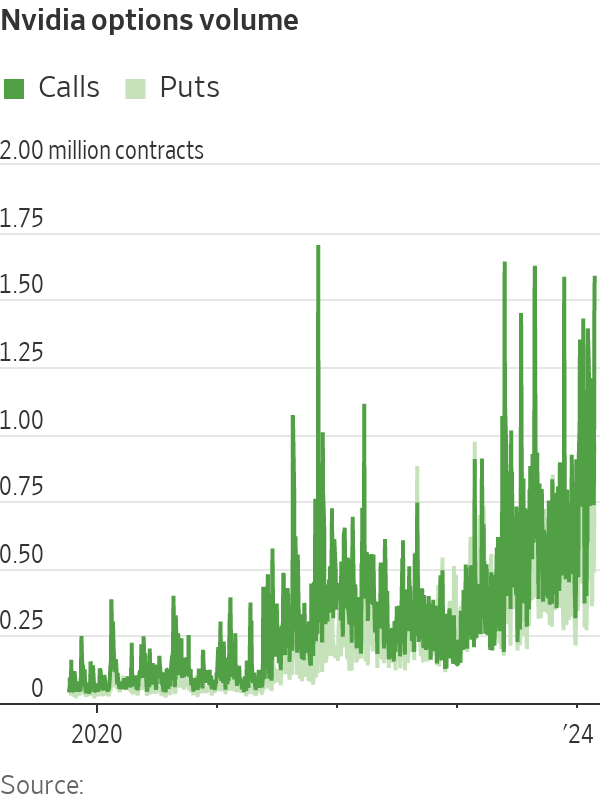
Ahead of the tech behemoth’s earnings report Wednesday, options pegged to the shares jumping to $1,300 —around double where they were trading at the time—were some of the most popular trades.
And for some investors, the 16% one-day jump in Nvidia’s share price Thursday wasn’t enough. They sought even bigger returns and piled into several niche exchange-traded funds that offer magnified exposure to Nvidia stock.
The GraniteShares 2x Long NVDA Daily ETF has taken in almost half a billion dollars from investors on a net basis since launching late in 2022. The fund’s shares have more than doubled in 2024 and have surged nearly 650% since inception.
There have been few signs of profit-taking so far. Investors added a net $263 million to the fund in the past month. The fund’s cousin, which turbocharges bearish bets against Nvidia, has been much less popular.
The euphoria surrounding Nvidia has spread to other stocks, too. Shares of Super Micro Computer , a much smaller company worth less than $50 billion, popped more than 30% Thursday after Nvidia’s earnings report. Traders spent more than $5 billion on options tied to the company, more than what they spent on Tesla this week. Tesla is worth about 13 times as much as the company.
Nvidia’s continued, rapid ascent has stunned even early bulls on semiconductors and generative AI.
Atreides Management founder Gavin Baker, who started covering Nvidia as an analyst at Fidelity in 2000, reminded investors in his Boston hedge fund in an early 2021 letter of Marc Andreessen ’s adage that software was eating the world. “Today, AI is replacing software,” he wrote.
Atreides started buying Nvidia shares in the fourth quarter of 2022, according to regulatory filings.
The wager proved profitable. But as Nvidia shares kept soaring, Baker started selling. Atreides was out of Nvidia by the end of the second quarter of 2023. “This has been a painful mistake,” Baker wrote in a June 2023 letter to his clients, when Nvidia was trading north of $420 a share.
Atreides’s stake in competitor Advanced Micro Devices has helped alleviate the pain from missing out on larger gains. The firm made nearly a quarter billion last year alone on AMD, which it continues to hold along with several other related bets.
Michael Hannosh, a 20-year-old college student in Chicago, said he first purchased shares of Nvidia in August 2022, when the stock traded below $180. Nvidia was one of his first-ever stock purchases. He had built a custom computer for videogaming and used a lot of Nvidia parts.
Hannosh said he kept the shares until last March, then sold them for a roughly 30% profit. He later bought a few more shares at about $230 and sold them over the course of the next several days at a profit.
The shares have tripled since.
“It’s blown my f—ing mind to bits. It’s insane,” said Hannosh. “I really wish I held it, obviously.”
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
Subsidised minivans, no income taxes: Countries have rolled out a range of benefits to encourage bigger families, with no luck
Imagine if having children came with more than $150,000 in cheap loans, a subsidised minivan and a lifetime exemption from income taxes.
Would people have more kids? The answer, it seems, is no.
These are among the benefits—along with cheap child care, extra vacation and free fertility treatments—that have been doled out to parents in different parts of Europe, a region at the forefront of the worldwide baby shortage. Europe’s overall population shrank during the pandemic and is on track to contract by about 40 million by 2050, according to United Nations statistics.
Birthrates have been falling across the developed world since the 1960s. But the decline hit Europe harder and faster than demographers expected—a foreshadowing of the sudden drop in the U.S. fertility rate in recent years.
Reversing the decline in birthrates has become a national priority among governments worldwide, including in China and Russia , where Vladimir Putin declared 2024 “the year of the family.” In the U.S., both Kamala Harris and Donald Trump have pledged to rethink the U.S.’s family policies . Harris wants to offer a $6,000 baby bonus. Trump has floated free in vitro fertilisation and tax deductions for parents.
Europe and other demographically challenged economies in Asia such as South Korea and Singapore have been pushing back against the demographic tide with lavish parental benefits for a generation. Yet falling fertility has persisted among nearly all age groups, incomes and education levels. Those who have many children often say they would have them even without the benefits. Those who don’t say the benefits don’t make enough of a difference.
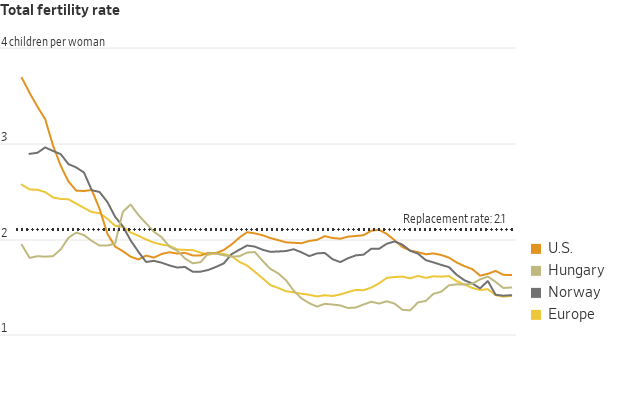
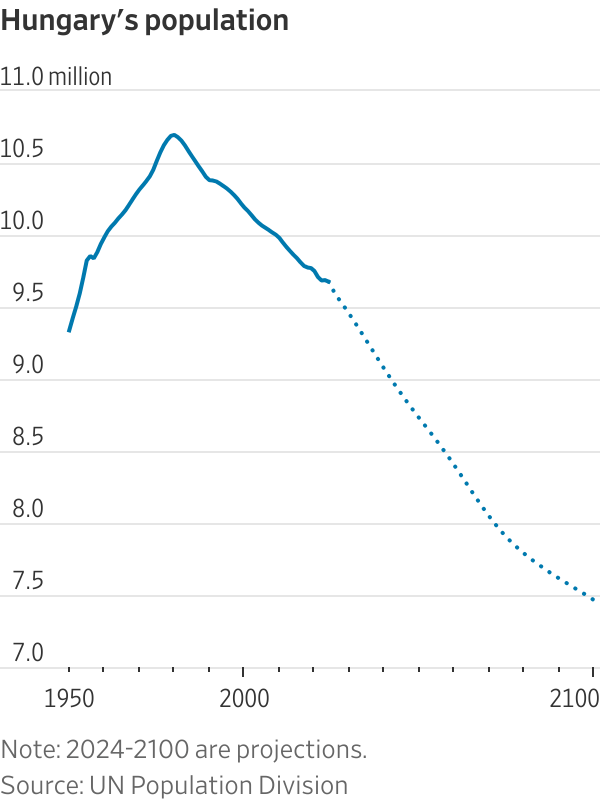
Two European countries devote more resources to families than almost any other nation: Hungary and Norway. Despite their programs, they have fertility rates of 1.5 and 1.4 children for every woman, respectively—far below the replacement rate of 2.1, the level needed to keep the population steady. The U.S. fertility rate is 1.6.
Demographers suggest the reluctance to have kids is a fundamental cultural shift rather than a purely financial one.
“I used to say to myself, I’m too young. I have to finish my bachelor’s degree. I have to find a partner. Then suddenly I woke up and I was 28 years old, married, with a car and a house and a flexible job and there were no more excuses,” said Norwegian Nancy Lystad Herz. “Even though there are now no practical barriers, I realised that I don’t want children.”
Both Hungary and Norway spend more than 3% of GDP on their different approaches to promoting families—more than the amount they spend on their militaries, according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
Hungary says in recent years its spending on policies for families has exceeded 5% of GDP. The U.S. spends around 1% of GDP on family support through child tax credits and programs aimed at low-income Americans.
Hungary’s subsidised housing loan program has helped almost 250,000 families buy or upgrade their homes, the government says. Orsolya Kocsis, a 28-year-old working in human resources, knows having kids would help her and her husband buy a larger house in Budapest, but it isn’t enough to change her mind about not wanting children.
“If we were to say we’ll have two kids, we could basically buy a new house tomorrow,” she said. “But morally, I would not feel right having brought a life into this world to buy a house.”
Promoting baby-making, known as pro natalism, is a key plank of Prime Minister Viktor Orbán ’s broader populist agenda . Hungary’s biennial Budapest Demographic Summit has become a meeting ground for prominent conservative politicians and thinkers. Former Fox News anchor Tucker Carlson and JD Vance, Trump’s vice president pick, have lauded Orbán’s family policies.
Orbán portrays having children inside what he has called a “traditional” family model as a national duty, as well as an alternative to immigration for growing the population. The benefits for child-rearing in Hungary are mostly reserved for married, heterosexual, middle-class couples. Couples who divorce lose subsidised interest rates and in some cases have to pay back the support.
Hungary’s population, now less than 10 million, has been shrinking since the 1980s. The country is about the size of Indiana.
“Because there are so few of us, there’s always this fear that we are disappearing,” said Zsuzsanna Szelényi, program director at the CEU Democracy Institute and author of a book on Orbán.
Hungary’s fertility rate collapsed after the fall of the Soviet Union and by 2010 was down to 1.25 children for every woman. Orbán, a father of five, and his Fidesz party swept back into power that year after being ousted in the early 2000s. He expanded the family support system over the next decade.
Hungary’s fertility rate rose to 1.6 children for every woman in 2021. Ivett Szalma, an associate professor at Corvinus University of Budapest, said that like in many other countries, women in Hungary who had delayed having children after the global financial crisis were finally catching up.
Then progress stalled. Hungary’s fertility rate has fallen for the past two years. Around 51,500 babies have been born there this year through August, a 10% drop compared with the same period last year. Many Hungarian women cite underfunded public health and education systems and difficulties balancing work and family as part of their hesitation to have more children.
Anna Nagy, a 35-year-old former lawyer, had her son in January 2021. She received a loan of about $27,300 that she didn’t have to start paying back until he turned 3. Nagy had left her job before getting pregnant but still received government-funded maternity payments, equal to 70% of her former salary, for the first two years and a smaller amount for a third year.
She used to think she wanted two or three kids, but now only wants one. She is frustrated at the implication that demographic challenges are her responsibility to solve. Economists point to increased immigration and a higher retirement age as other offsets to the financial strains on government budgets from a declining population.
“It’s not our duty as Hungarian women to keep the nation alive,” she said.
Hungary is especially generous to families who have several children, or who give birth at younger ages. Last year, the government announced it would restrict the loan program used by Nagy to women under 30. Families who pledge to have three or more children can get more than $150,000 in subsidised loans. Other benefits include a lifetime exemption from personal taxes for mothers with four or more kids, and up to seven extra annual vacation days for both parents.
Under another program that’s now expired, nearly 30,000 families used a subsidy to buy a minivan, the government said.
Critics of Hungary’s family policies say the money is wasted on people who would have had large families anyway. The government has also been criticised for excluding groups such as the minority Roma population and poorer Hungarians. Bank accounts, credit histories and a steady employment history are required for many of the incentives.
Orbán’s press office didn’t respond to requests for comment. Tünde Fűrész, head of a government-backed demographic research institute, disagreed that the policies are exclusionary and said the loans were used more heavily in economically depressed areas.
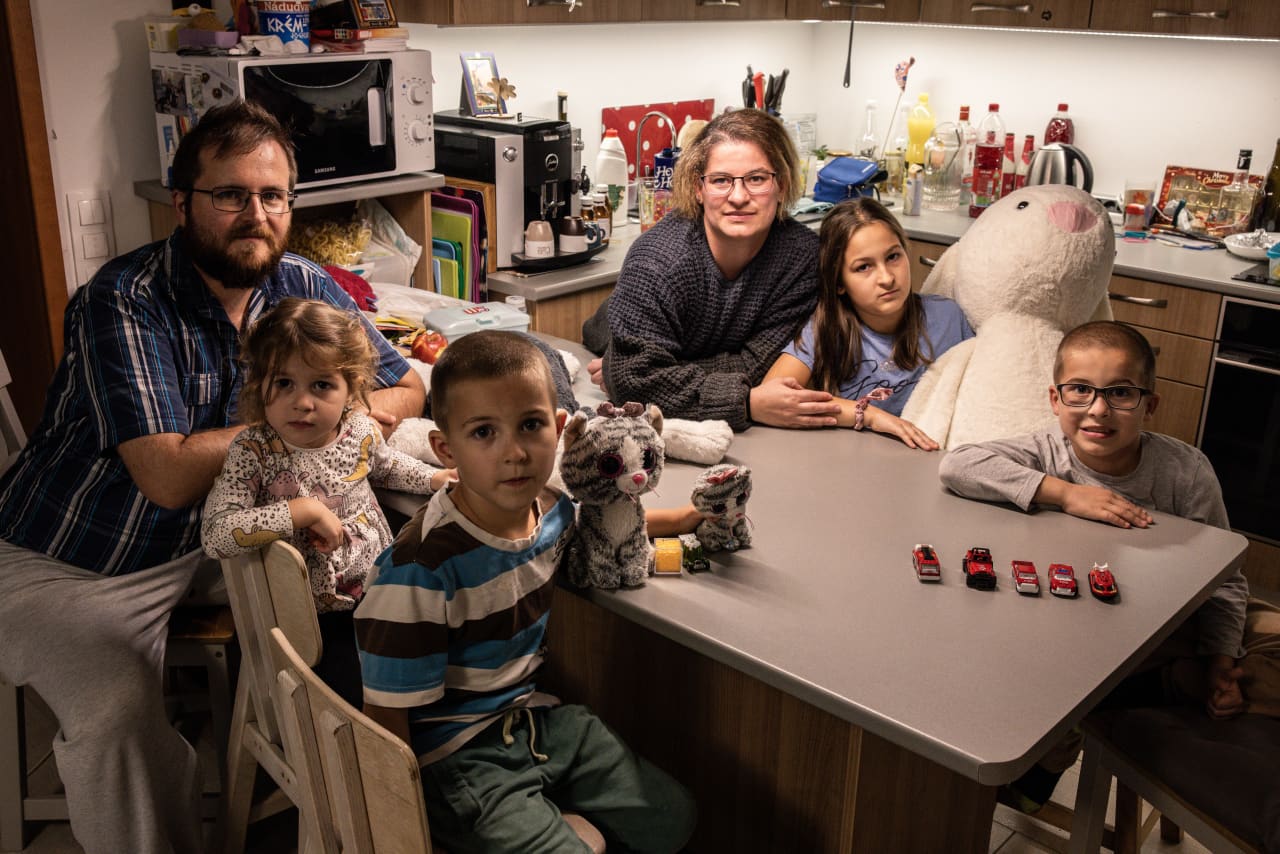

Government programs weren’t a determining factor for Eszter Gerencsér, 37, who said she and her husband always wanted a big family. They have four children, ages 3 to 10.
They received about $62,800 in low-interest loans through government programs and $35,500 in grants. They used the money to buy and renovate a house outside of Budapest. After she had her fourth child, the government forgave $11,000 of the debt. Her family receives a monthly payment of about $40 a month for each child.
Most Hungarian women stay home with their children until they turn 2, after which maternity payments are reduced. Publicly run nurseries are free for large families like hers. Gerencsér worked on and off between her pregnancies and returned full-time to work, in a civil-service job, earlier this year.
She still thinks Hungarian society is stacked against mothers and said she struggled to find a job because employers worried she would have to take lots of time off.
The country’s international reputation as family-friendly is “what you call good marketing,” she said.

Norway has been incentivising births for decades with generous parental leave and subsidised child care. New parents in Norway can share nearly a year of fully paid leave, or around 14 months at 80% pay. More than three months are reserved for fathers to encourage more equal caregiving. Mothers are entitled to take at least an hour at work to breast-feed or pump.
The government’s goal has never been explicitly to encourage people to have more children, but instead to make it easier for women to balance careers and children, said Trude Lappegard, a professor who researches demography at the University of Oslo. Norway doesn’t restrict benefits for unmarried parents or same-sex couples.
Its fertility rate of 1.4 children per woman has steadily fallen from nearly 2 in 2009. Unlike Hungary, Norway’s population is still growing for now, due mostly to immigration.
“It is difficult to say why the population is having fewer children,” Kjersti Toppe, the Norwegian Minister of Children and Families, said in an email. She said the government has increased monthly payments for parents and has formed a committee to investigate the baby bust and ways to reverse it.
More women in Norway are childless or have only one kid. The percentage of 45-year-old women with three or more children fell to 27.5% last year from 33% in 2010. Women are also waiting longer to have children—the average age at which women had their first child reached 30.3 last year. The global surge in housing costs and a longer timeline for getting established in careers likely plays a role, researchers say. Older first-time mothers can face obstacles: Women 35 and older are at higher risk of infertility and pregnancy complications.
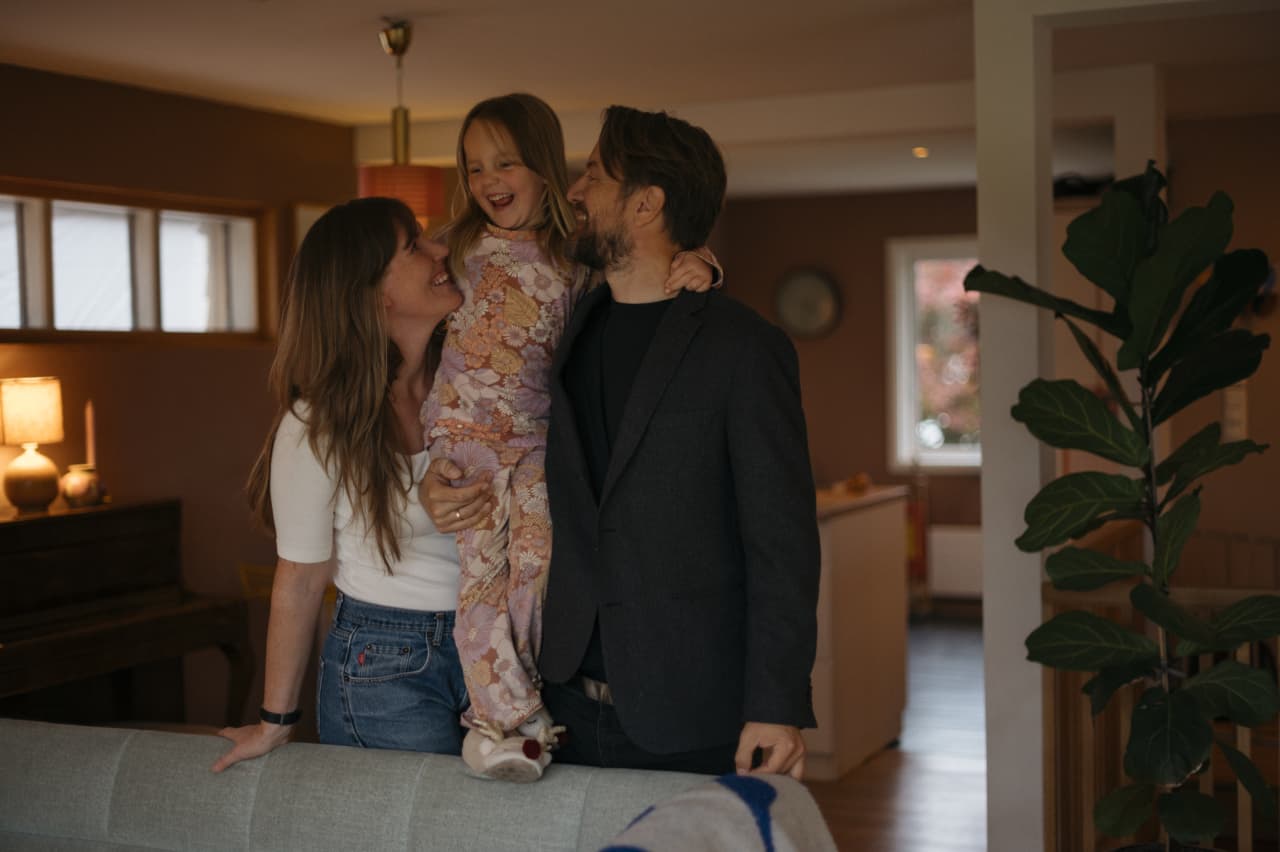
Gina Ekholt, 39, said the government’s policies have helped offset much of the costs of having a child and allowed her to maintain her career as a senior adviser at the nonprofit Save the Children Norway. She had her daughter at age 34 after a round of state-subsidised IVF that cost about $1,600. She wanted to have more children but can’t because of fertility issues.
She receives a monthly stipend of about $160 a month, almost fully offsetting a $190 monthly nursery fee.
“On the economy side, it hasn’t made a bump. What’s been difficult for me is trying to have another kid,” she said. “The notion that we should have more kids, and you’re very selfish if you have only had one…those are the things that took a toll on me.”
Her friend Ewa Sapieżyńska, a 44-year-old Polish-Norwegian writer and social scientist with one son, has helped her see the upside of the one-child lifestyle. “For me, the decision is not about money. It’s about my life,” she said.