China Restricts Some Steel Production
How that will weigh on iron-ore demand.
How that will weigh on iron-ore demand.
China’s efforts to drastically reduce pollution levels could lead to lower demand for iron ore, a raw material for the steel industry, which is a big source of the nation’s harmful emissions.
It hasn’t happened yet, however. “With the Chinese economy almost fully recovered from the pandemic, demand for steel is very strong,” which means that demand for iron ore is also very strong, says John Kartsonas, a managing partner at Breakwave Advisors, the advisor for the Breakwave Dry Bulk Shipping exchange-traded fund (ticker: BDRY).
At the same time, iron-ore supply remains tight, with Brazil, a major producer of the commodity, not fully recovered from a deadly accident two years ago that hurt production, he says. In 2019, Vale halted some mining operations following a fatal dam breach in Brazil, leading to significant declines in its iron-ore output. Vale pegged its production of iron-ore fines at 300.4 million metric tons in 2020, compared with nearly 384.2 million metric tons in 2018.
Tight supplies and rising demand helped lift the most-active futures contract for 62% iron-ore fines delivered to China to US$174.94 per metric ton on March 4, the highest settlement since August 2011, based on Dow Jones Market Data reports going back to October 2010. That’s not far from the record-high settlement of US$188.88 from February 2011.
China produced more than one billion metric tons of crude steel last year, and there are “no iron-ore projects that will produce sizeable net new tons for at least five years,” says Paul Bartholomew, a metals analyst at S&P Global Platts. Expectations for further Chinese economic stimulus are also positive for steel and iron-ore demand, he says.
Iron-ore prices, however, have eased in recent days on prospects of a slowdown in demand, as China plans to reduce factory activity to cut carbon emissions. The March contract was at US$168.26 on March 16, trading 2.6% lower month to date.
Tangshan, a city in China’s Hebei province referred to as the nation’s steelmaking hub, has ordered factories to limit or halt production on days when a heavy-pollution alert is in place, to cut overall emissions by 50%, according to the South China Morning Post.
“Steelmaking is a major source of pollution in China, estimated to account for about 15% of the country’s total emissions, so it is hardly surprising investors took profits at the prospect the steel industry could be facing significant environmental controls,” says Stuart Burns, editor at large for metals analysis provider MetalMiner. “The first casualty of reduced steel production would be demand for raw materials,” he says.
Still, China might not be able to fully implement restrictions on steel production. Reducing steel output may be “difficult to achieve this year,” says Bartholomew. In the past, many facilities taken offline were already “mothballed or uneconomic,” he says. “It’s harder to close production when mills are operating and making money.”
The VanEck Vectors Steel ETF (SLX), which provides exposure to companies involved in the steel sector, has climbed about 10% this month.
Given China’s restrictions on operations of some highly pollutant steel mills, however, Breakwave’s Kartsonas says he is now “a bit more cautious” on the outlook for iron-ore prices.
Brazil has signalled an increase in iron-ore production. That, in combination with China’s pollution restrictions, could lead to “more moderate” prices in the next several months, he says. Still, if demand for construction continues to support steel, that means iron-ore prices can remain “higher than historical averages for a long time.”
Reprinted by permission of Barron’s. Copyright 2021 Dow Jones & Company. Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. Original date of publication: March 18, 2021
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
Move over, Marvel. The next blockbuster entertainment franchise might come from Japan.
Anime is shaping up as the country’s next big export industry, beyond cars and electronics. This once-niche entertainment form is entering the worldwide mainstream , and its growth could light up investors’ portfolios.
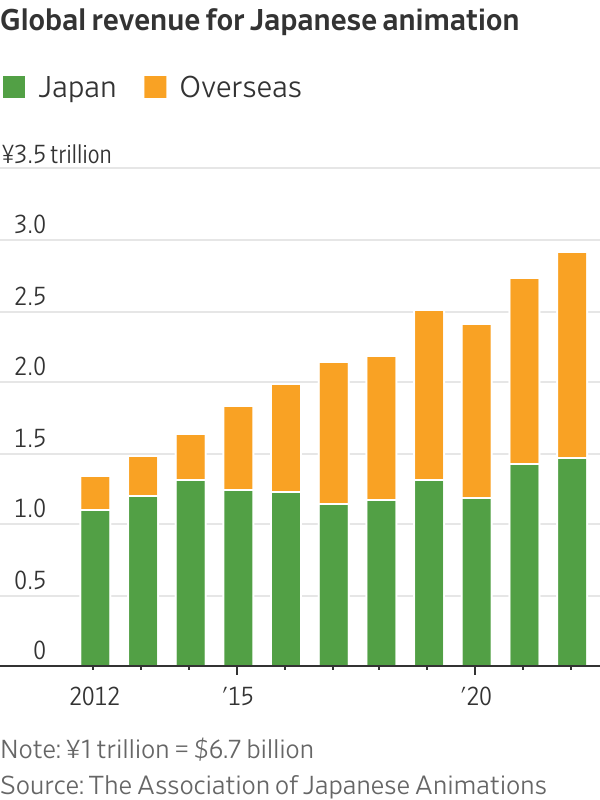
The global market for Japanese animation, known as anime, and its related products has more than doubled between 2012 and 2022 to 2.9 trillion yen, equivalent to $20 billion, according to the Association of Japanese Animations. The overseas market has been driving that growth. Markets outside of Japan made up around half of the total in 2022, compared with around 18% a decade earlier.
Streaming companies such as Netflix are certainly taking notice. Its live-action series “One Piece,” based on a Japanese comic, was its most-watched show in the second half of 2023. In fact, anime content on Netflix in the period logged 14% viewing growth from the first half of 2023, compared with a 4% drop overall, according to Jefferies. These streaming platforms will continue to introduce more anime-related content to their global audiences.
Japan’s anime and manga, the Japanese word for comics, have created many well-known characters and franchises over the years, such as Pokémon. And it looks to be getting even more mainstream. The anime market in North America has grown from $1.6 billion in 2018 to $4 billion this year, according to Jefferies. And Asia, which has long been more receptive to anime, will likely continue to grow strongly, especially in China. Anime has also been popular on Chinese streaming platforms such as Bilibili .
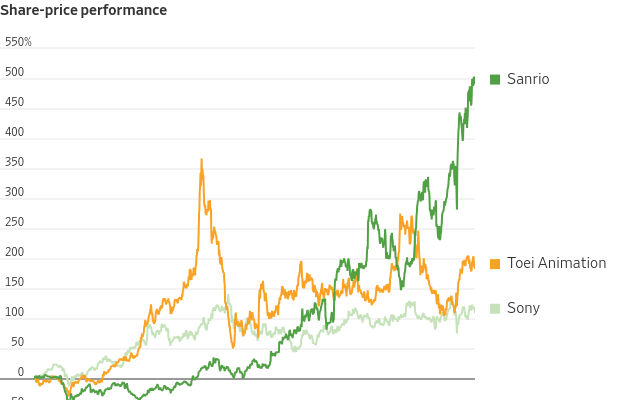
Apart from streaming, selling merchandise can be even more lucrative. Sanrio , which owns characters like Hello Kitty , has reported record profits, with its share price rising nearly sixfold over the past five years.
Sony would be another major beneficiary of this trend . The company owns animation streaming service Crunchyroll, which had 15 million subscribers as of June. That compared with around 3 million subscribers when Sony announced the acquisition of the streaming service from AT&T for nearly $1.2 billion in 2020. This contrasts with Sony’s approach in online streaming for other content: It acts more like an “arms dealer,” selling movies and shows to platforms such as Netflix and Amazon.com . That means the company could benefit more directly from the anime boom. And anime also has strong synergies with its movie and game businesses .
Anime maker Toei Animation, which owns popular franchises such as “One Piece” and “Dragon Ball,” is another listed company that would benefit. It makes anime itself, but more important for the overseas markets, it also earns licensing revenue from the copyrights to popular franchises that it owns. Sales outside of Japan accounted for more than half of its total revenue in the latest fiscal year ended in March. Season two for Netflix’s “One Piece” is already in production. Toei stock has nearly tripled since the end of 2019.
Anime has blockbuster potential, not just for audiences but for investors as well.