China’s Overcapacity Is Already Backfiring
Excess investment in industry isn’t made up by trading partners, and it has domestic consequences
Excess investment in industry isn’t made up by trading partners, and it has domestic consequences
In the “ China Shock 2.0 ” narrative, not only is China a security threat and a low-end factory competitor, but it is also angling to swamp the West with cut-rate high-tech goods. There has been less focus on the downsides of such a strategy for China itself.
China’s first-quarter growth beat most estimates , rising 5.3% on the year—thanks mostly to strong industrial output and exports. But the economic data released Tuesday also showed that excess capacity is very real, and could be damaging to China itself.
While China’s industrial engine revved up in January and February , it downshifted again in March: output rose just 4.5% on the year, down sharply from January and February’s 7%. More tellingly, manufacturing capacity utilisation plummeted to 73.8% in the first quarter—its weakest, excluding the pandemic-affected first quarter of 2020, since at least 2015. In volume terms, China’s exports hit a nearly 10-year high in March. But in value terms they were barely above where they sat in October.
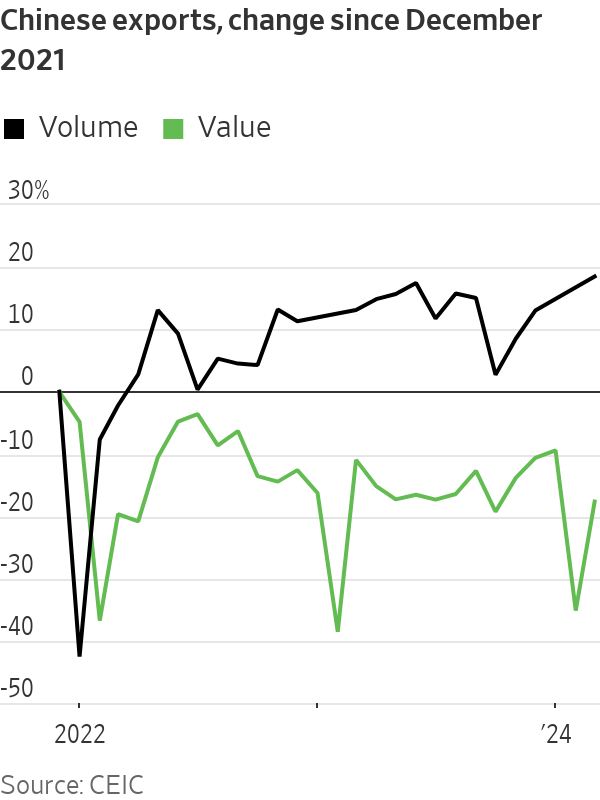
In other words, firms’ pricing power both at home and abroad is weakening and margin pressure is probably mounting: The March industrial financial data, which will be released later this month, will be worth watching.
So will private investment in manufacturing. If external demand, in value terms, doesn’t find a stronger footing soon and China’s domestic economy remains weak, then eventually such investment will need to slow. Otherwise the government, or state-owned banks, will have to start absorbing the cost of too many loans to industry more directly, as they already have with real estate and infrastructure.
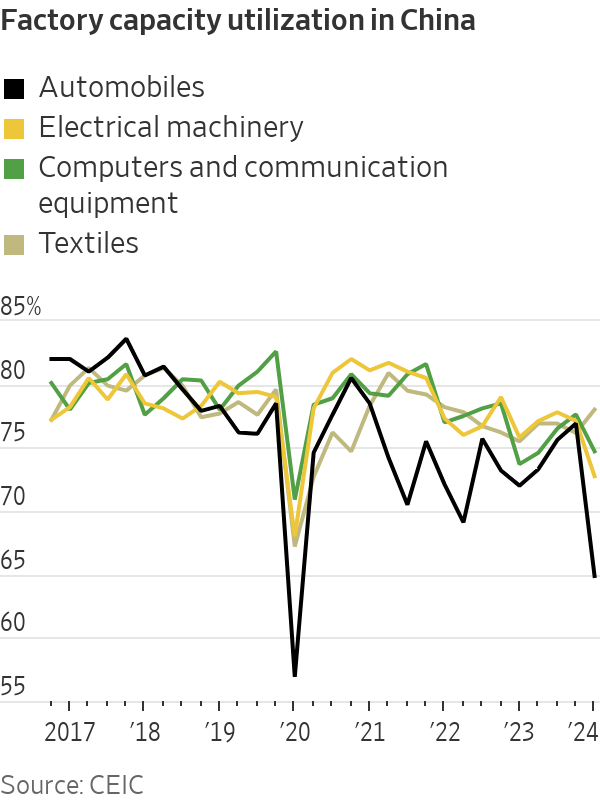
Particularly interesting is the breakdown of that capacity utilisation data itself. Falling run rates were especially obvious in Beijing’s favourite sectors like automobiles and electrical equipment—the so-called “new productive forces,” including electric vehicles, chips and solar panels, which policymakers have highlighted in recent speeches and have been stalking Western politicians’ nightmares. Automobile manufacturing utilisation rates fell below 65% in the first quarter: well below their previous low (excluding the first quarter of 2020) of 69.1% in mid-2016.
China’s traditional export sectors, on the other hand, have actually held up relatively well. Textiles utilisation rose in the first quarter, while run rates for computer and communication gear fell, but much less sharply.
Meanwhile, economy wide borrowing—excluding government bond issuance—weakened further in March, despite bond yields and interest rates near multiyear lows. If margin pressure starts to force some “new productive forces” to start slowing investment, fiscal policy would need to step in to prop up growth.
Alternatively, China can keep funnelling its excess savings into new manufacturing overcapacity—but Chinese banks and Beijing, not just China’s trade partners, will eventually end up footing the bill.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
The sports-car maker delivered 279,449 cars last year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
A long-standing cultural cruise and a new expedition-style offering will soon operate side by side in French Polynesia.
The sports-car maker delivered 279,449 cars last year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
Porsche car deliveries fell 10% in 2025 as demand was hit by a slowdown in luxury spending in China and as it ceased production of its 718 Boxster and 718 Cayman models through the year.
The German luxury sports-car maker said Friday that it delivered 279,449 cars in the year, down from 310,718 in 2024.
The company had a tumultuous year as it contended with a stuttering transition to electric vehicles and a tough Chinese market, while the Trump administration’s automotive tariffs presented a further headwind.
Deliveries in its largest sales region of North America were virtually flat at 86,229, but continued challenges in China meant deliveries in the country dropped 26% to 41,938 vehicles.
Automakers have faced intense competition in China, sparking a prolonged price war as rivals cut prices to win customers, while a lengthy property market slump and economic-growth concerns in the country has also led to buyers pulling back on luxury spending.
“Key reasons for the decline remain the challenging market conditions, particularly in the luxury segment, and the very intense competition in the Chinese market, especially for all-electric models,” the company said.
Other German brands including Audi, BMW and Mercedes-Benz have all recently reported that the challenging Chinese market hit demand last year.
In Europe, Porsche deliveries fell 13% to 66,340 cars excluding its home market of Germany, while German deliveries dropped 16%.
The company cut guidance several times last year as it warned of hits from U.S. import tariffs, investments in new combustion engines and hybrid models amid the slow uptake of EVs, and the competitive situation in China.
Porsche also last year announced plans to scale back its EV ambitions and instead expand its lineup with more gas-powered and plug-in hybrid models than it had originally planned.
However, in its statement Friday, the company said it increased its share of electrified-vehicle deliveries in the year. Around 34% of vehicles delivered worldwide were electrified, an increase of 7.4 percentage points on year, with about 22% all-electric vehicles and 12% plug-in hybrids.
That leaves its global share of fully-electric vehicles at the upper end of its target range of 20% to 22% for 2025.
In Europe, for the first time in 2025, more electrified vehicles than purely combustion engine vehicles were delivered.
The Macan topped the delivery charts in the year, while the 911 reached a record high with 51,583 deliveries worldwide, it said.
Porsche said it is investing in its three-pronged powertrain strategy and will continue to respond to increasing demand for personalization requests from customers.
“We have a clear focus for 2026,” Sales and Marketing Chief Matthias Becker said. “We want to manage supply and demand in accordance with our ‘value over volume’ strategy.
“At the same time, we are realistically planning our volume for 2026 following the end of production of the 718 and Macan with combustion engines.”