Bank of Japan Raises Rate, Halts Emergency Policies
Central bank says stable inflation is in sight and ends unconventional asset purchases
Central bank says stable inflation is in sight and ends unconventional asset purchases
TOKYO—The Bank of Japan on Tuesday ended negative interest rates after eight years and unwound most of its unorthodox monetary easing policies, saying a new era of stable inflation is in sight in Japan.
The decision marks the end of a global era of negative interest rates that began in the 2010s. Other central banks that had introduced negative rates in the 2010s, including the European Central Bank and the Swiss National Bank , have already moved back into positive territory amid inflation triggered by the Covid-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine.
For a generation, the Japanese central bank served as a laboratory for monetary-policy experimentation as it addressed the country’s chronic stagnation, which was marked by flat or falling prices.
On Tuesday, BOJ Gov. Kazuo Ueda said those policies have fulfilled their roles and the principal ones will be ended. The Bank of Japan is moving its key target for short-term rates to a range of 0% to 0.1%, its first rate increase since 2007.
Ueda said the move was justified by steadily rising wages and prices in Japan. The central bank “judged that sustainable and stable achievement of our 2% inflation goal has come into sight,” he said.
The BOJ said it removed a target for the yield on 10-year Japanese government bonds. And it is halting its purchases of assets such as stocks, real-estate investment trusts and corporate bonds that don’t typically go onto the books of central banks. The Bank of Japan has amassed the equivalent of hundreds of billions of dollars in such assets since the global financial crisis of 2008-09.
Market reaction was restrained because Bank of Japan officials had telegraphed their intentions. The Nikkei Stock Average closed up 0.7%, while the yen was down.
The Bank of Japan, which had maintained a negative policy rate since 2016, said it would continue buying government bonds.
“Accommodative financial conditions will likely continue, and these accommodative financial conditions will firmly support the economy and prices,” Ueda said at a news conference. He said he didn’t expect to raise interest rates rapidly.
Prime Minister Fumio Kishida welcomed the continuation of easy money, saying it was too soon to declare an end to deflation.
The BOJ had already begun to ease away from its unconventional policies. In September 2016, it set a target of around zero for the yield on 10-year government bonds. After initially enforcing that target strictly, the bank last year loosened its control , allowing the yield to move higher amid a surge in global bond yields. As of late Tuesday, the 10-year yield was 0.725%.
The Bank of Japan’s move to restore traditional monetary policy tools is one example of how Japan’s economy has recently reverted to conditions not seen in more than three decades.
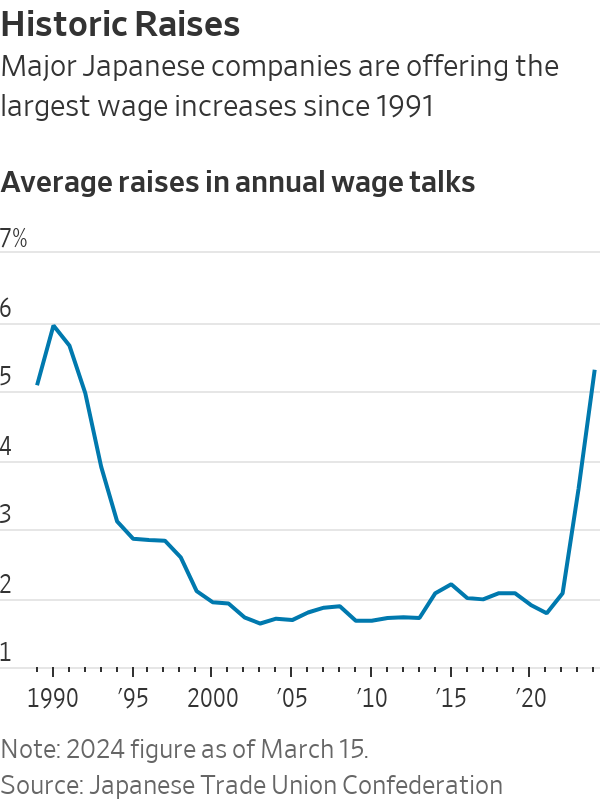
In February, the Nikkei Stock Average hit a record for the first time in 34 years. Japan’s largest labor union said last week that major companies are planning to raise pay by an average of 5.28% this year, the largest increase since 1991.
However, the Bank of Japan’s economic assessment pointed to some warning signs. With China’s economy struggling recently , the BOJ said Japan’s economy “is expected to be under downward pressure stemming from a slowdown in the pace of recovery in overseas economies.”
Two of the BOJ’s nine-member policy board dissented from the decision to end negative rates, saying the economy’s recovery was too fragile to allow for a rate increase.
Katsutoshi Inadome, senior strategist at SuMi Trust, said the BOJ probably saw a window to act after the recent good news on wages, but he said there was a chance Tuesday’s rate increase was premature.
“In a textbook approach, this is timing the bank would have done better to avoid,” Inadome said. He pointed to sluggish consumption in Japan, which Ueda acknowledged as a risk.
Ueda said if the economy received shocks in the future, the central bank would consider using policy tools it has used previously.
“The Bank of Japan is unlikely to make additional rate increases because there will gradually appear more headwinds such as the lack of strength in prices,” said Mizuho Securities chief market economist Yasunari Ueno.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”