The chiefs of America’s biggest companies reached new pay heights in 2023 as stock awards swelled the value of compensation packages.
Half of the executives in a Wall Street Journal analysis made at least $15.7 million, a record for median CEO pay in the annual survey, with several making more than $50 million . Median pay for the same companies a year earlier was about $14.5 million .
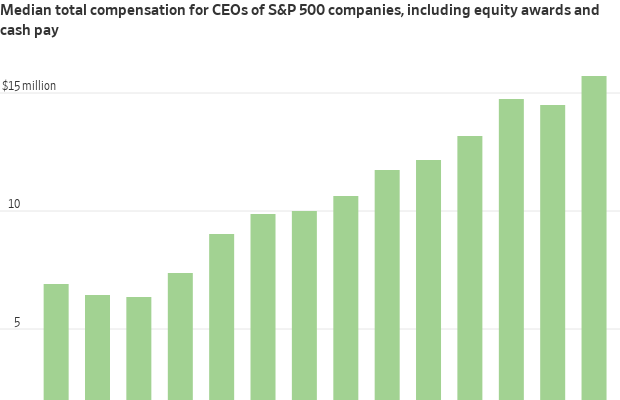
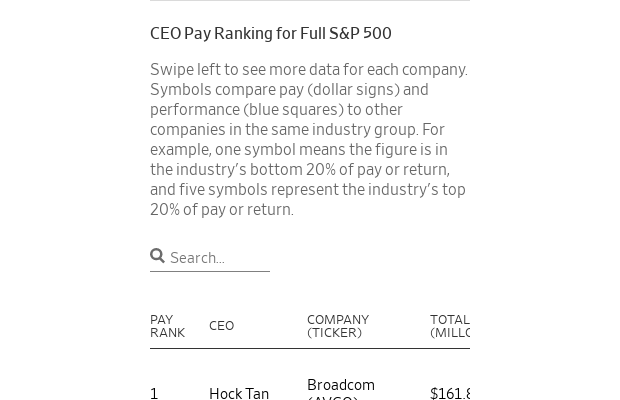
Most of the executives received year-over-year raises of at least 9%—one in four got 25% or more—and most companies recorded annual shareholder returns of at least 13%, the Journal found in an analysis of data on more than 400 companies from MyLogIQ , a provider of public-company data and analysis. (See the full ranking below.)
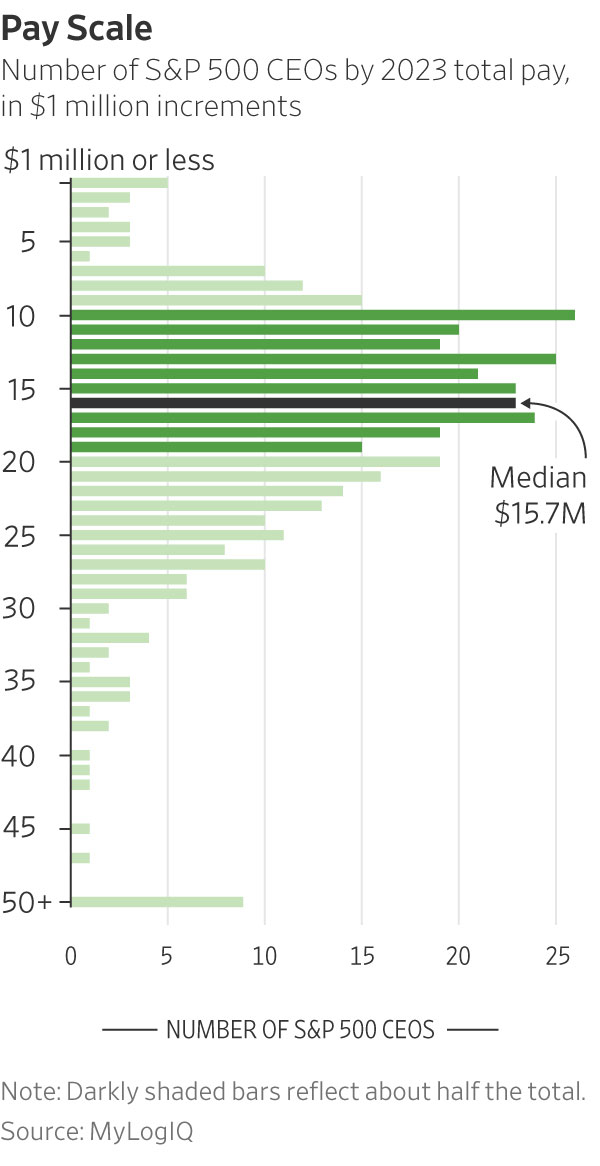
Eight tech executives ranked among the 25 top earners, as did five each heading financial companies and media or entertainment companies.
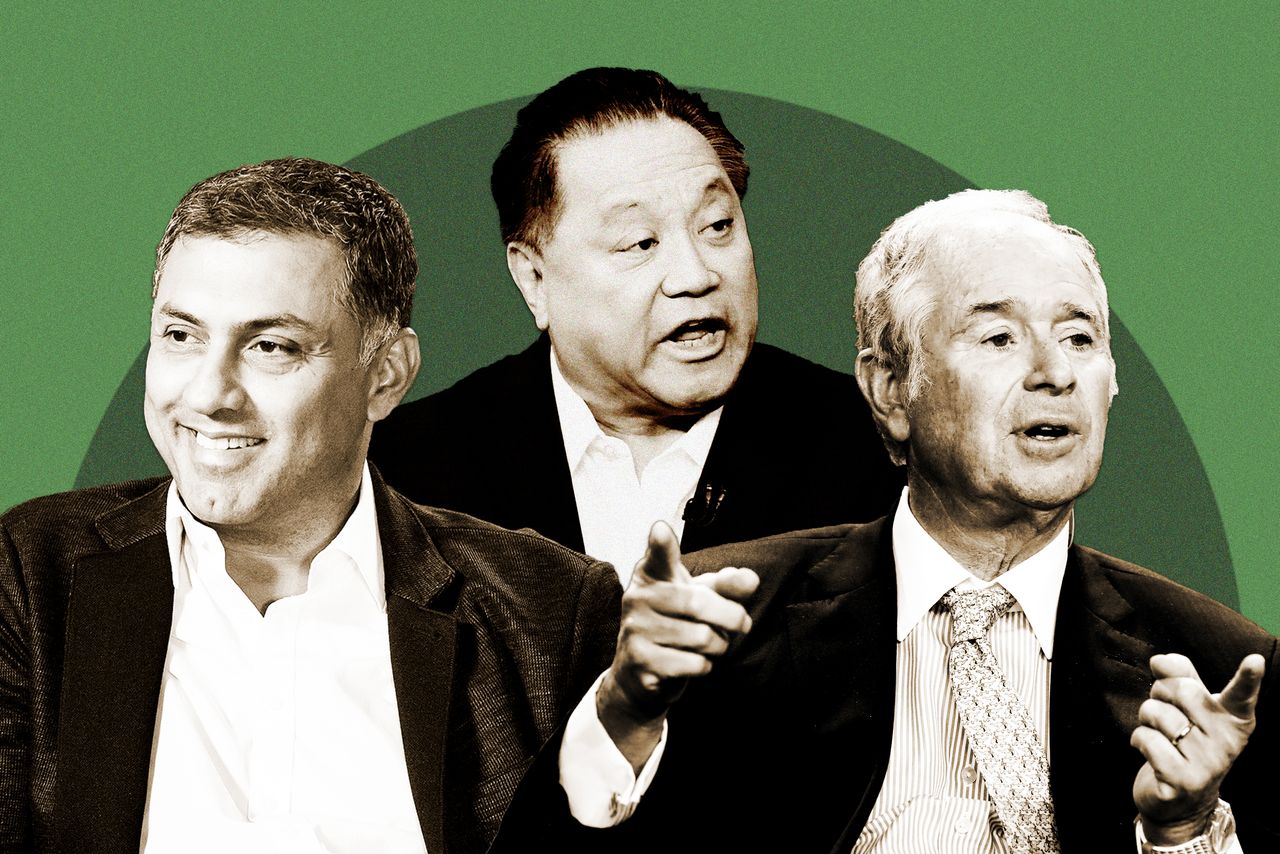
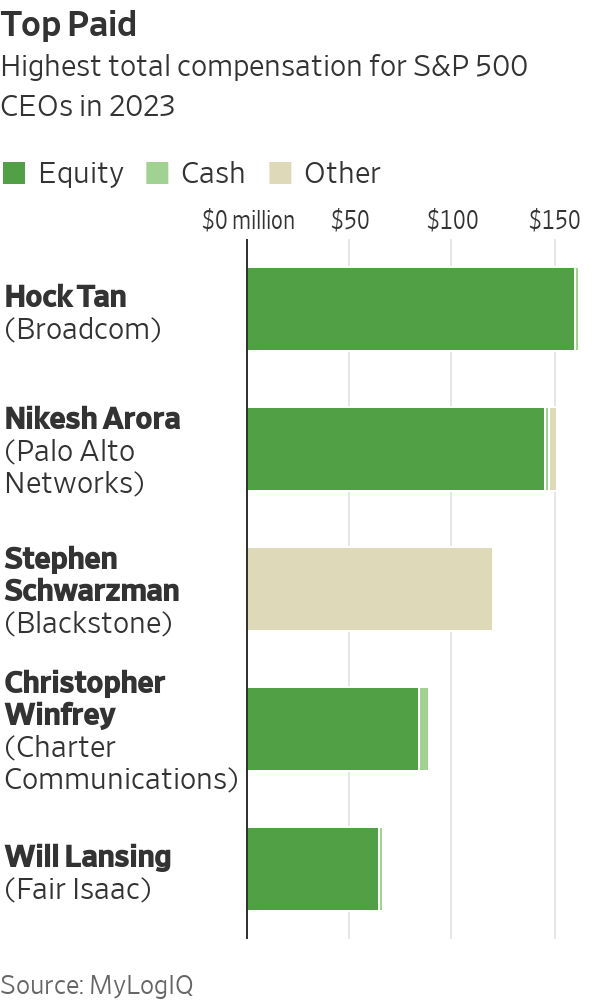
Hock Tan , the highest-paid CEO in the Journal’s analysis at $162 million, has to stay on the job for five years and Broadcom ’s share price must reach certain targets after October 2025 to get the full value of most of his pay. Broadcom said the company has outperformed competitors under Tan, its CEO since 2006, and he won’t get more equity or cash bonuses for five years.
Pay for Nikesh Arora at Palo Alto Networks totalled $151 million, mostly in equity awards that included shares granted over three years.
Blackstone , where Steven Schwarzman made $120 million, said the company’s 83% total return surpassed U.S. asset managers last year and described its pay structure as aligning executive incentives with those of investors.
Christopher Winfrey of Charter Communications , the cable operator, received total pay valued at $89.1 million, largely in options and stock vesting over five years, and much of it only if the company’s shares rise 28% to 152% from when the grants were made.
A $30 million one-time retention and leadership award that vests over five years helped boost total pay for Fair Isaac ’s Will Lansing to $66 million. The company said its shareholder returns ranked among the top 1% of companies in the S&P 500 over the past decade.
Stock gains
Equity awards continued to make up the bulk of most executives’ pay, much of it structured to deliver more stock or options if the company meets financial or share-price performance over several years. That means the pay can lose considerable value if the company’s share price falls or operating targets are missed—or soar in value amid market and operating success.
Restricted stock awarded in early March last year to Jensen Huang , CEO of graphics-chip maker Nvidia , quadrupled in value through late January, to $107.5 million. Huang’s pay, originally reported at $34.2 million , included $26.7 million of restricted stock as valued at grant.
Under the terms of the award, Huang could receive 50% to 100% more shares than originally targeted if the company meets performance criteria, according to Nvidia’s proxy.
Nvidia’s share price tripled during the year.
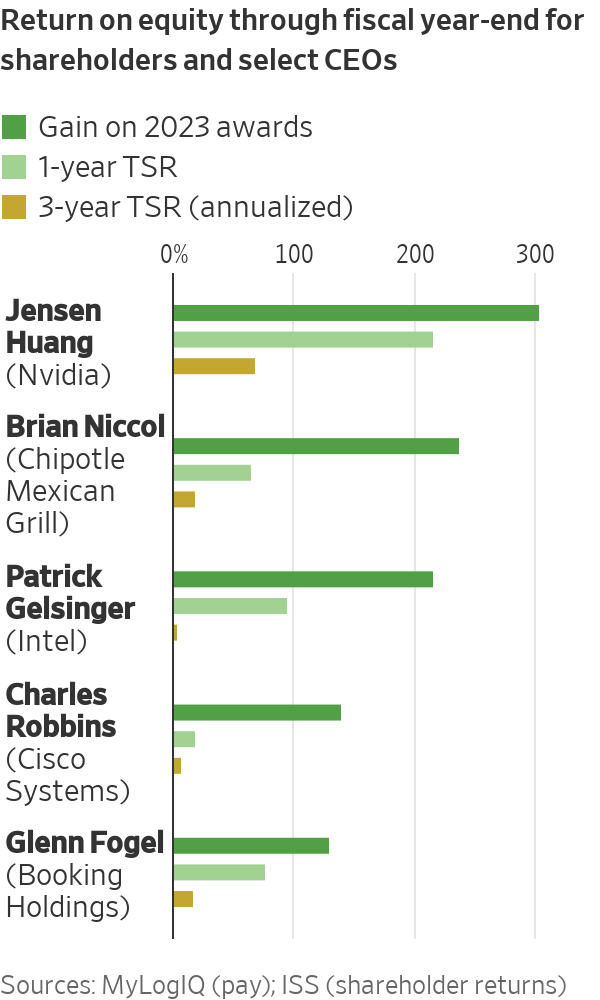
Brian Niccol , CEO of restaurateur Chipotle Mexican Grill , received stock and options valued at $15.5 million when they were granted in February 2023 as part of a $22.5 million pay package. By the end of the year, that equity had more than tripled in value, to $52.2 million, the company said. Chipotle shares returned about 65% during 2023, and 18% a year over three years.
A Chipotle spokeswoman said the growth in Niccol’s equity-award value reflects the company’s strong share-price performance during the year. The company said the value Niccol ultimately realises depends on continued financial, operating and stock-market performance by the company.
Intel CEO Patrick Gelsinger ’s equity awards last year also more than tripled in value by year-end, to $39.3 million. The company said in its securities filings that austerity measures last year reduced Gelsinger’s salary by about 15% to $1.1 million, which in turn reduced his cash bonus target by about 15%, to $2.9 million.
Overall, median cash pay for CEOs, including salary and annual bonuses, remained flat at about $3.8 million.
Top performers
Pay for CEOs running the best- and worst-performing companies didn’t vary dramatically. Median total pay was $14.6 million for the 20% of CEOs whose companies recorded the worst returns compared with other companies in the same sector, and $15.7 million for CEOs at the best-performing companies.
Chip and computer hardware makers accounted for six of the 25 best-performing companies—including Nvidia, the top performer—while four were in the travel or transportation industries. Several of the top performers bounced back from one or more years of poor returns, often tied to the pandemic.
Royal Caribbean Group reported paying Jason Liberty $17.2 million and recorded a total return of 162% last year, after posting minus 36% in 2022 and minus 43% in 2020, when the cruise industry was battered by illness and travel bans. (The company posted a 3% return in 2021.) Ride-sharing giant Uber Technologies recorded a 149% return after posting returns of minus 41% in 2022 and minus 18% in 2021.
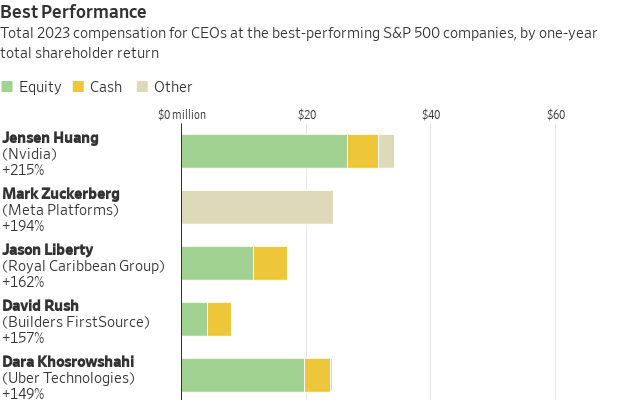
Chip maker Advanced Micro Devices , ranked seventh by one-year performance, was headed by Lisa Su , the second-highest-paid woman in the analysis, at just over $30 million, including nearly $28 million in restricted stock and options. The highest-paid woman, at $31.55 million, was Julie Sweet of consultant Accenture , which posted a one-year total return of about 14%.
Thirty-one women ran S&P 500 companies for the full year of 2023, up from around two dozen at the beginning of the decade. None ranked among the top 25 by pay. One other woman ran one of the 25 best performers: Jayshree Ullal at networking company Arista Networks , which posted a 94% return. Ullal’s pay totalled $15.56 million.
Bottom of the pack
Among the 25 worst-performing companies in the Journal analysis, nearly a third operated in the healthcare sector, including six pharmaceutical or biotech companies. They were joined by four utilities.
Pfizer said it didn’t pay bonuses to top executives last year after weak demand for Covid-related products led the company to miss financial targets. The $17.5 million equity award that made up most of CEO Albert Bourla ’s total pay last year is meant to recognize his leadership and give him an incentive to focus on long-term strategy, the company said.
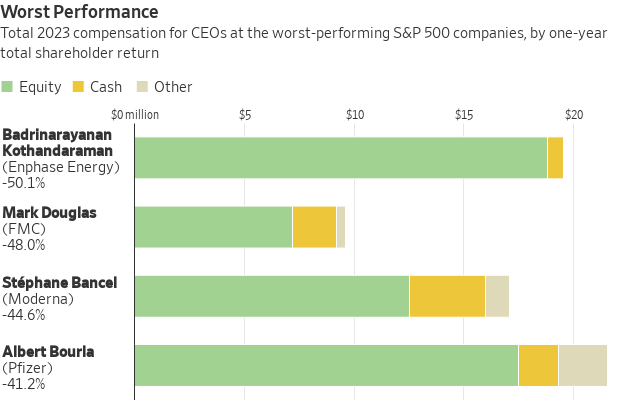
Poor performance can slash the value of CEO equity awards. Covid-vaccine maker Moderna reported total pay of $17.1 million for CEO Stéphane Bancel last year, including $12.5 million in stock and option awards.
The value of those awards fell 42% to $7.3 million at year-end, the company’s proxy shows, as Moderna’s stock price tumbled about the same amount for the year. In addition, equity awards made to Bancel in prior years fell in value by about $167 million during 2023.
Those losses offset a net $945 million in new equity awards and increases in value reported for Bancel during the prior three years.
Moderna declined to comment.
Methodology
The Wall Street Journal used data from corporate proxy statements filed through May 16 by companies in the S&P 500 index with fiscal years ended after June 30, 2023. The data was collected by MyLogIQ, a provider of public-company data and analysis.
Aggregate pay and shareholder-return figures exclude companies that changed CEOs or fiscal-year-end dates during the year.
Pay reflects the value of equity awards at grant, as reported by companies. Total returns reflect stock-price change and dividends, in most cases calculated from the month end closest to the company’s fiscal-year end.
Sources: MyLogIQ (compensation); Institutional Shareholder Services, FactSet (shareholder return); Standard & Poor’s (industry groups); company filings (pay for select companies)
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
What a quarter-million dollars gets you in the western capital.
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
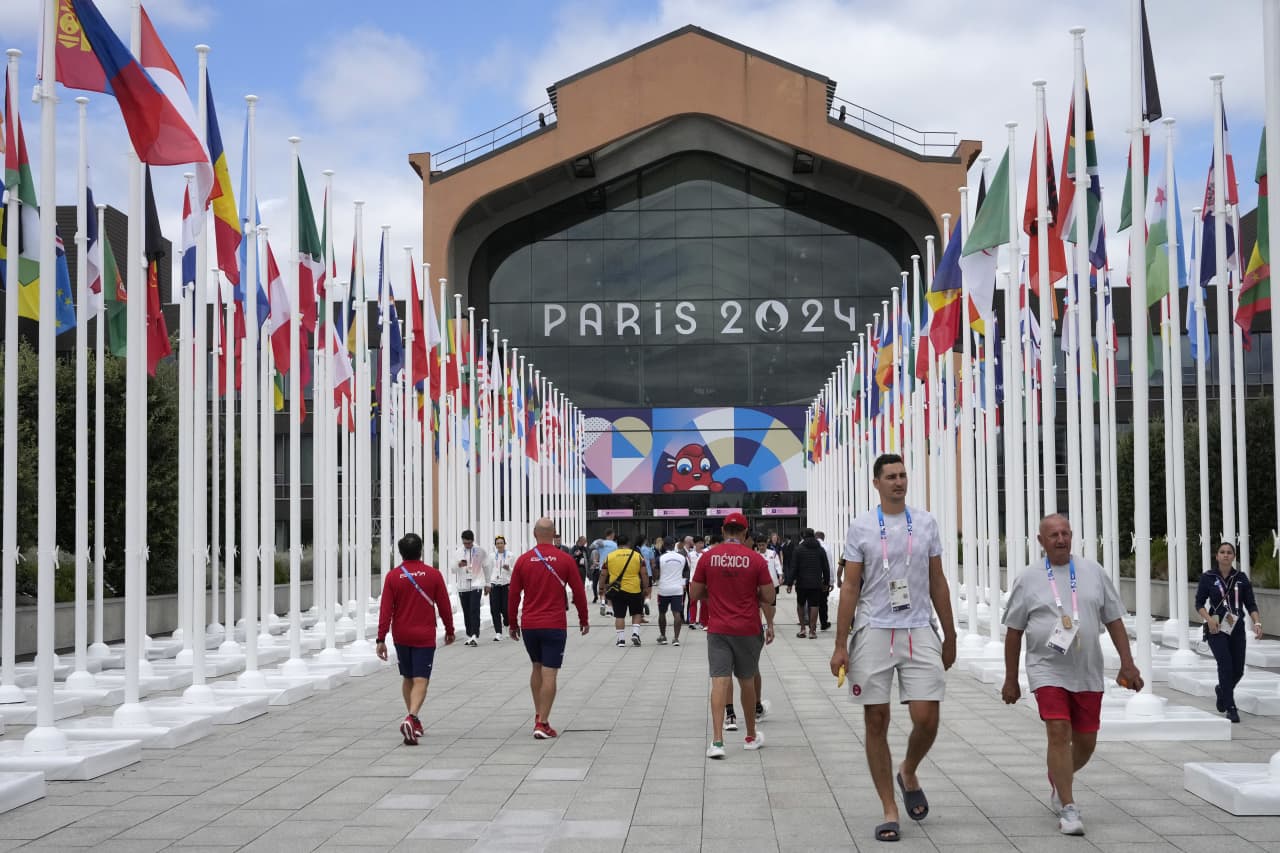
As Paris makes its final preparations for the Olympic games, its residents are busy with their own—packing their suitcases, confirming their reservations, and getting out of town.
Worried about the hordes of crowds and overall chaos the Olympics could bring, Parisians are fleeing the city in droves and inundating resort cities around the country. Hotels and holiday rentals in some of France’s most popular vacation destinations—from the French Riviera in the south to the beaches of Normandy in the north—say they are expecting massive crowds this year in advance of the Olympics. The games will run from July 26-Aug. 1.
“It’s already a major holiday season for us, and beyond that, we have the Olympics,” says Stéphane Personeni, general manager of the Lily of the Valley hotel in Saint Tropez. “People began booking early this year.”
Personeni’s hotel typically has no issues filling its rooms each summer—by May of each year, the luxury hotel typically finds itself completely booked out for the months of July and August. But this year, the 53-room hotel began filling up for summer reservations in February.
“We told our regular guests that everything—hotels, apartments, villas—are going to be hard to find this summer,” Personeni says. His neighbours around Saint Tropez say they’re similarly booked up.
As of March, the online marketplace Gens de Confiance (“Trusted People”), saw a 50% increase in reservations from Parisians seeking vacation rentals outside the capital during the Olympics.
Already, August is a popular vacation time for the French. With a minimum of five weeks of vacation mandated by law, many decide to take the entire month off, renting out villas in beachside destinations for longer periods.
But beyond the typical August travel, the Olympics are having a real impact, says Bertille Marchal, a spokesperson for Gens de Confiance.
“We’ve seen nearly three times more reservations for the dates of the Olympics than the following two weeks,” Marchal says. “The increase is definitely linked to the Olympic Games.”

Getty Images
According to the site, the most sought-out vacation destinations are Morbihan and Loire-Atlantique, a seaside region in the northwest; le Var, a coastal area within the southeast of France along the Côte d’Azur; and the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean.
Meanwhile, the Olympics haven’t necessarily been a boon to foreign tourism in the country. Many tourists who might have otherwise come to France are avoiding it this year in favour of other European capitals. In Paris, demand for stays at high-end hotels has collapsed, with bookings down 50% in July compared to last year, according to UMIH Prestige, which represents hotels charging at least €800 ($865) a night for rooms.
Earlier this year, high-end restaurants and concierges said the Olympics might even be an opportunity to score a hard-get-seat at the city’s fine dining.
In the Occitanie region in southwest France, the overall number of reservations this summer hasn’t changed much from last year, says Vincent Gare, president of the regional tourism committee there.
“But looking further at the numbers, we do see an increase in the clientele coming from the Paris region,” Gare told Le Figaro, noting that the increase in reservations has fallen directly on the dates of the Olympic games.
Michel Barré, a retiree living in Paris’s Le Marais neighbourhood, is one of those opting for the beach rather than the opening ceremony. In January, he booked a stay in Normandy for two weeks.
“Even though it’s a major European capital, Paris is still a small city—it’s a massive effort to host all of these events,” Barré says. “The Olympics are going to be a mess.”
More than anything, he just wants some calm after an event-filled summer in Paris, which just before the Olympics experienced the drama of a snap election called by Macron.
“It’s been a hectic summer here,” he says.

AFP via Getty Images
Parisians—Barré included—feel that the city, by over-catering to its tourists, is driving out many residents.
Parts of the Seine—usually one of the most popular summertime hangout spots —have been closed off for weeks as the city installs bleachers and Olympics signage. In certain neighbourhoods, residents will need to scan a QR code with police to access their own apartments. And from the Olympics to Sept. 8, Paris is nearly doubling the price of transit tickets from €2.15 to €4 per ride.
The city’s clear willingness to capitalise on its tourists has motivated some residents to do the same. In March, the number of active Airbnb listings in Paris reached an all-time high as hosts rushed to list their apartments. Listings grew 40% from the same time last year, according to the company.
With their regular clients taking off, Parisian restaurants and merchants are complaining that business is down.
“Are there any Parisians left in Paris?” Alaine Fontaine, president of the restaurant industry association, told the radio station Franceinfo on Sunday. “For the last three weeks, there haven’t been any here.”
Still, for all the talk of those leaving, there are plenty who have decided to stick around.
Jay Swanson, an American expat and YouTuber, can’t imagine leaving during the Olympics—he secured his tickets to see ping pong and volleyball last year. He’s also less concerned about the crowds and road closures than others, having just put together a series of videos explaining how to navigate Paris during the games.
“It’s been 100 years since the Games came to Paris; when else will we get a chance to host the world like this?” Swanson says. “So many Parisians are leaving and tourism is down, so not only will it be quiet but the only people left will be here for a party.”















